TITLE 1 -- COMMITTEE ON AGRICULTURE
10001 - THRIFTY FOOD PLAN
The "Thrifty Food Plan was developed by the USDA to provide a healthy diet for families on a limited budget. It is the basis for the SNAP program. According to this plan the Secretary of Agriculture (currently Brooke Rollins) can adjust requirements for qualification on October 1st of each year based on cost adjustments.
10002 - ABLE BODIED ADULTS WITHOUT DEPENDENTS WORK REQUIREMENTS
This section talks about who is exempt (i.e. pregnant, mentally/physically unfit), but the bottom line says "exceptions in subparagraphs F through H shall cease to have an effect on October 1, 2030. This includes currently homeless, veterans, (and) 24 and under who were in foster care or under the responsibility of the state."
10003 - ABLE BODIED ADULTS WITHOUT DEPENDENTS WAIVERS
An amendment to paragraph 4 of the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008, which deals with reenrollment requirements for SNAP, specifically who is eligible. It states that "...the average monthly number of exemptions...during a fiscal year does not exceed 1% of the number of covered individuals in the State." (This is amended down from 8%.)
10004 - AVAILABILITY OF STANDARD UTILITY ALLOWANCES BASED ON RECEIPT OF ENERGY ASSISTANCE
Amending the Food and Nutrition Act of 2008 to specify not all households qualify, but just those with elderly or disabled members.
10005 - RESTRICTIONS ON INTERNET EXPENSES
A new section added to include that no internet fees can be used as a shelter expense deduction.
10006 - MATCHING FUNDS REQUIREMENTS
This deals with what the Secretary of Agriculture can allot to SNAP based on the State's payment error rate, and amends the percentages.
10007 - ADMINISTRATIVE COST SHARING
Amendment to change the wording so that the Secretary is authorized to now pay each State agency 25% of all administrative costs involved in providing SNAP, instead of 50% as it was before.
10008 - GENERAL WORK REQUIREMENT AGE
Age ranges for this work-requirement section have been changed from 15 to 60, to now 17 to 65, who are no longer eligible for SNAP. Work requirements for someone with a child under the age of 6, has been amended to "under the age of 7," and the exemptions for a child between the ages of 1 and 6, is now also 1 and 7.
10009 - NATIONAL ACCURACY CLEARINGHOUSE
An amendment was added to include data-sharing for those on SNAP, in order to prevent dual applications for assistance across multiple states.
10010 - QUALITY CONTROL ZERO TOLERANCE
An erasure of the previous allowable error amount of $37, to now be $0.
10011 - NATIONAL EDUCATION AND OBESITY PREVENTION GRANT PROGRAM REPEALER
Total removal of the nutrition education and obesity prevention program for eligible individuals.
10012 - ALIEN SNAP ELIGIBILITY
An amendment to change who is allowed to participate in SNAP. Those who entered the U.S. prior to 1948 now do not qualify, unless they came from Cuba.
10013 - EMERGENCY FOOD ASSISTANCE
Amendment to the Emergency Food Assistance Act of 1983 to extend the time allotted for transfer of $4 million in emergency food assistance from 2024 to 2031.
B - INVESTMENT IN RURAL AMERICA
10101 - SAFETY NET
This section amends the Agricultural Act of 2014 to change the term "references prices" to equate to specific prices per bushel for wheat, corn, sorghum, barley, oats, et al. After the year 2031 these process will be multiplied by 1.005, not to exceed 115%. Extensions from 2023 to 2031 for most regulations. Limits of not more than 30 million base acres to be included in these regulations per eligible farms. All eligibility for allotted base acres is determined through a "five-year average," which includes acreage planted, and any prevention of planting due to natural disaster. For new owners, the Secretary of Agriculture will consider planting history. Losses in unborn livestock are eligible for compensation. Emergency assistance for livestock, farmed fish, and honeybees.
10102 - CONSERVATION
Amending portions of the Food Security Act of 1985 to extend through 2031. Reducing $5 million just $1 million for the Grassroots Source Water Program. Reducing $50 million to $10 million for the Voluntary Public Access and Habitat Incentive Program. Amending portions of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 to include reducing $75 million for the Feral Swine Eradication and Control Pilot Program to $15 million. Adding funding to fiscal years 2026 through 2031. Doing the same for funds from the Commodity Credit Corporation.
10103 - SUPPLEMENTAL AGRICULTURAL TRADE PROMOTION PROGRAM
The Secretary will conduct a program to encourage expansion of commercial export markets for agriculture, and use funds from the Commodity Credit Corporation.
10104 - RESEARCH
In reference to the Food, Agriculture, Conservation and Trade Act of 1990, amending years to extend through 2031. In reference to the Agricultural Act of 2014 and as pertains to the Foundation for Food and Agriculture Research, amended to reduce funds from $200 million to "remain available under expended" to $37 million "no later than 30 days after the date of enactment." In reference to scholarships for students at 1890s institutions, which did provide full tuition, employment, employee benefits, fees, books, and room and board for up to 4 years, is now $60,000 total until expended. In reference to the Assistive Technology Program for Farmers with Disabilities, funds increased from $6 million to $8 million "until expended." Specialty Crop Research Initiative increased from $80 million to $175 million after 2025. For the Research Facilities Act, there will now be a specified grant program, $125 million for each fiscal year beginning in 2026.
10105 - SECURE RURAL SCHOOLS; FORESTRY
If any county in any state has already received their 25% payment for 2024, this will be deducted from future payments. The same for 50%. All dates updated from 2023 to 2026, as per the Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act of 2000. All dates updated from 2025 to 2028. Any dates listed as 2026 are now 2029. Competitive grants for non-federal forest landowners are rescinded. For state and private forestry conservation programs, $100,719,676 are rescinded.
10106 - ENERGY
Biobased Markets Program dates in the Farm Security and Rural Investment Act of 2002 are updated from 2024 to 2031. Bioenergy Program for Advanced Biofuels dates are updated from 2024 to 2031.
10107 - HORTICULTURE
Funding increased for Plant Pest and Disease Management and Disaster Prevention Program from $63 million to $75 million for 2018 through 2025. Year updated from 2018 to 2026, with increased funding from $75 million to $90 million. The Specialty Crop Block Grant funding will increase from $72.9 million (2023) to $85 million for 2018 through 2025, and will increase to $100 million in 2026. The Organic Production and Market Data Initiative will increase from $1 million (2024) to $10 million for fiscal years 2026 through 2031. Funding used for modernization and improvement of International Trade Technology Systems and Data Collection will increase from $1 million (2024 & 2025) to $5 million in 2026. Funding leftover from the Multiple Crop and Pesticide Use Survey will be used until expended.
10108 - MISCELLANEOUS
Funding for Animal Disease Prevention and Management, as per the Animal Health Protection Act, will increase from $30 million for fiscal years 2023 through 2025, to $233 million per each fiscal year 2026 through 2030, from the Commodity Credit Corporation.
Funding for the Sheep Production and Marketing Grant Program will increase from $2 million to $3 million, and all dates will be changed from 2024 to 2031.
TITLE 2 -- COMMITTEE ON ARMED SERVICES
20001 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF LIVE FOR MILITARY PERSONNEL
This section covers an appropriation of funds to the Secretary of Defense (currently Pete Hegseth) for the fiscal year of 2025, that will remain available until September 30, 2029. This includes a total cost of $7,315,480,000 in added funding for things like Space Force sustainment, incentive pay, Non-Traditional Education Support's Online Academic Skills Course program, Department of Defense Impact Aid payments (financial assistance for schools impacted by presence of military dependent students), and Armed Forces retirement home facilities.
20002 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR SHIPBUILDING
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $33,751,301,000 for things like production of turbine generators, U.S.-made steel plates, new submarines, new Guided Missile Destroyers (DDGs), a San Antonio-class Amphibious Transport Dock, and new shipbuilding facilities.
20003 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR INTEGRATED AIR AND MISSILE DEFENSE
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $18,833,000,000 for Next Generation Missile Defense Technologies (for interception and expanding range of defense systems) and $5,913,000,000 for Layered Homeland Defense.
20004 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR MUNITIONS AND DEFENSE SUPPLY CHAIN RESILIENCY
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $20,195,700,000 for things like development, procurement, and integration of underwater explosives, lightweight torpedoes, large-diameter solid rocket motors for hypersonic missiles, and acceleration of Army next-generation shoulder-fired air defense systems. In addition, there will also be $500,000,000 appropriated to the Department of Defense Credit Program Account, which provides loans and technical assistance for critical minerals and related industries and projects.
20005 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR SCALING LOW-COST WEAPONS INTO PRODUCTION
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $12,524,000,000 for things like improvements to Test Resource Management Center AI capabilities, expansion of Cyber Command AI lines of effort, and low-cost cruise missiles. In addition, there will also be $1,000,000,000 appropriated to the Department of Defense Credit Program Account.
20006 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY AND CYBERSECURITY OF THE DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE
An additional appropriation of $380,000,000 to replace business systems, deploy automation and AI, improve budgetary and programmatic infrastructure, and purchase defense cybersecurity programs.
20007 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR AIR SUPERIORITY
This section covers appropriation of funds for the aforementioned time period of fiscal year 2025, and available until September 30, 2029. This includes a total cost of $7,270,680,000 to buy more F-15EX aircraft, prevent retirement of F-22s, accelerate F-47 production, and increase the production of Advanced Aerial Sensors.
20008 - ENHANCEMENT OF RESOURCES FOR NUCLEAR FORCES
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $9,675,300,000 for things like expansion of D5 missile motor production, acceleration of the B-21 long-range bomber aircraft, risk-reduction activities for the Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missile program, and increased production of MH-139 helicopters. This section also includes appropriations for the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) in the amount of $3,240,000,000 for performing NNSA Phase 1 studies, accelerating construction of NNSA facilities, and accelerating domestic uranium enrichment centrifuge deployment.

20009 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES TO IMPROVE CAPABILITIES OF UNITED STATES INDO-PACIFIC COMMAND
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $11,118,600,000 for things like Army exercises and operations in the Western Pacific, revitalization of existing Arctic naval infrastructure, intelligence capabilities for U.S. Africa Command, improvements to the Space Force, and funding for anti-submarine sonar arrays.
20010 - ENHANCEMENT OF DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE RESOURCES FOR IMPROVING THE READINESS OF THE ARMED FORCES
This section covers appropriation of funds for the same time period. This includes a total cost of $11,546,000,000 for upgrades to Marine Corps utility helicopters, Air Force depot modernization, OPN-8 maritime spares and repair, and procurement of Army wheeled combat wheels and anti-lock braking systems.
20011 - IMPROVING DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE BORDER SUPPORT AND COUNTER DRUG MISSIONS
This section specifies $5,000,000,000 set aside for border operations, including deployment of military personnel and temporary detention of migrants.
20012 - ENHANCEMENT OF MILITARY INTELLIGENCE PROGRAMS
This section specifies $2,000,000,000 for the enhancement of military intelligence programs.
20013 - DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE OVERSIGHT
This section specifies $10,000,000 for data-management and ownership within the Department of Defense, including programs involving classified matters.
20014 - MILITARY CONSTRUCTION PROJECTS AUTHORIZED
This section appropriates (unspecified) funds for military construction, land acquisition, and military family housing.
20015 - PLAN REQUIRED
This section says that the Secretary of Defense and the Administrator of the National Nuclear Security Agency (currently Teresa Robbins) should submit any spending reports or operations plans no later than 45 days after the enactment of this bill.
20016 - LIMITATION ON AVAILABILITY OF FUNDS
This section states that all funds listed in sections 20001 through 20016 cannot be disbursed after September 30, 2034.
Total spending for this portion of H.R. 1 is $150,273,061,000
TITLE 3 -- COMMITTEE ON EDUCATION AND WORKFORCE
30001 - STUDENT ELIGIBILITY
This portion of the bill refers to the Higher Education Act of 1965 and makes several amendments. These include revising any reference allowing for permanent residents of the U.S. or those able "to provide evidence from the Immigration and Naturalization Service that he or she is in the United States for other than a temporary purpose with the intention of becoming a citizen or permanent resident" and simplifying it down to just "citizens or nationals," lawfully-admitted "aliens," citizens of Cuba, and lawful residents in accordance with the Compact of Free Association (deals made with Pacific Island sovereign states). The amendment will take place on July 1, 2025 and will apply with respect to award year 2025-2026.
30002 - AMOUNT OF NEED; COST OF ATTENDANCE; MEDIAN COST OF COLLEGE
This section is in reference to the same Act and amends years of eligibility to '25-'26 and '26-'27). It includes semantics changes from "same academic workload" to "enrolled in the same program of study," etc., and updates to the years included in the bill. It also inserts a new section to clarify the "median cost of college" as the price of a program of study across all higher-education institutions. The amendment redefines "program of study" according to academic codes and credential level, undergraduate or graduate. Under "Exemption of Certain Assets," there is an amendment for family farms on which families reside, and small businesses owned and controlled by family. The amendment will take place on July 1, 2025 and will apply with respect to award year 2025-2026.
300011 - LOAN LIMITS
This section is in reference to the same Act and adds an amendment to eliminate subsidized Federal Stafford loans for undergraduate students, and Federal Direct Plus loans for graduate or professional students after July 1, 2026, and restrict parent borrowers on behalf of dependent students. The undergraduate annual loan limits is amended to be the difference of the median cost of the program of study (across all academic institutions, Harvard to the University of Montana) and the amount of Federal Pell Grant received. New loan limits are as follows: undergraduate $50,000, graduate $100,000, professional $150,000. If a student is not enrolled full-time, the loan limit will be in direct proportion to the percentage of credits. There is a 3-year exception for students who enroll prior to July 1, 2026.
30021 - LOAN REPAYMENT
This section is in reference to the same Act and discusses loan repayment plans with a start date of July 1, 2026. All repayment (whether borrowed before or after said date) will be required for outstanding loans. An amendment is included to change references of repayment of a "Federal Direct PLUS Loan" to "an excepted Consolidation Loan." There will now be two repayment plans: a standard plan of 10 - 25 years, and a repayment assistance plan. The latter replaces the "Income-Contingent" repayment plan, which allowed for flexible payments based on your income, instead of a fixed payment over the loan tenure. However, this includes assistance for distressed borrowers who are not able to make a full-payment in a given month, for which they will not accrue interest. The minimum monthly payment for assistance is $10. For a yearly adjusted gross income (AGI) of $10,000 a monthly payment is not more than $120, up to $20,000 not more than 1%, up to $30,000 not more than 2%, up to $40,000 not more than 3%, up to $50,000 not more than 4%, up to $60,000 not more than 5%, all the way up to more than $100,000 at 10% of AGI. All amendments apply "with respect to any borrower who is in repayment before, on, or after the date of enactment."
30022 - DEFERMENT; FORBEARANCE
This section is in reference to the same Act, and includes amendments to eliminate loan deferment after July 1, 2025 for unemployment and economic hardship, but allows for forbearance up to 9 months or if the borrower is serving in a medical or dental internship.
30023 - LOAN REHABILITATION
This section is in reference to the same Act and amends Federal Family Education, direct, and Perkins loans, allowing for loans in default to be rehabilitated twice instead of just once. This includes a minimum payment of $10/month.
30024 - PUBLIC SERVICE LOAN FORGIVENESS (PSLF)
This section is in reference to the same Act, amending who is considered a "public servant." Medical/dental internships and residency programs are no longer included in this subheading as of July 1, 2025. Repayment Assistance Plan payments now qualify as PSLF payments.
30025 - STUDENT LOAN SERVICING
This section is in reference to the same Act, and will provide additional mandatory funds of $500,000,000 to the Department of Education to cover administrative and student loan costs.
30031 - ELIGIBILITY
This section is in reference to the same Act, and makes amendments to the AGI of a student. This includes foreign income from the student, the student's parents, or the student's spouse. This section is also amended to define "full-time student" as completing 30 semester or trimester hours, or 45 quarter credit hours per awarded year. Students whose student aid index equals or exceeds twice the amount of the total maximum for the Pell Grant will no longer qualify, nor will students enrolled less than half-time, as of July 1, 2026.
30032 - WORKFORCE PELL GRANTS
This section is in reference to the same Act, and states that beginning July 1, 2026, and each subsequent year, eligible students enrolled in workforce programs can apply for Pell Grants. This includes clocking at least 150, but less than 600 hours of instruction between 8 and 15 weeks. The education must align with "high-wage, high-skill...or in-demand industry sectors or occupations." Graduate students are not eligible, though students working towards a graduate program are.
30033 - PELL SHORTFALL
This section is in reference to the same Act, and raises the appropriation of funds for 2026 from $2,170,000,000 to $5,351,000,000; for 2027 from $1,235,000,000 to $6,058,000,000; and adding $3,743,000,000 for 2028 and $1,236,000,000 for each succeeding fiscal year.
30041 - AGREEMENTS WITH INSTITUTIONS
This section is in reference to the same Act, and allows for institutions of higher education participating in direct student loan programs to request an annual reimbursement for the "non-repayment balance" from students who have defaulted on loans, beginning in award year 2028-2029. This includes undergraduate and graduate students who completed their studies, and those who did not. Special circumstances include students with two or more programs of study and certain consolidation loans. If an institution of higher education fails to notify the non-repayment balance within 3 months, they will be required to pay that balance. If they fail to notify for 12 months, they will become ineligible for future direct loans. If they fail to notify for 18 months, they will become ineligible for future direct loans and Federal Pell Grants. If they fail to notify for 2 years, the institution will be ineligible to participate in any program for 10 years.
30042 - CAMPUS-BASED AID PROGRAMS
This section is in reference to the same Act, and adds "Subpart 11-- Promoting Real Opportunities to Maximize Investments and Savings in Education."
420S - PROMISE GRANTS
This section states that the Secretary (currently Linda McMahon) will award PROMISE grants to eligible schools that submit "satisfactory application(s)."
420T - ELIGIBLE INSTITUTIONS; APPLICATION
In order to be eligible for a PROMISE grant an institution must meet the maximum total price guarantee requirements (i.e. locked tuition rates for a certain period of time), and describe how grant funds will be used and how they will collect and disseminate information on promising practices.
420U - GRANT AMOUNTS; FLEXIBLE USE OF FUNDS
This section discusses how the Secretary will determine the amount an institution receives for their PROMISE grant, an average based on the total amount awarded for the three previous years and the percentage of low-income students attending their school.
420V - AVAILABILITY OF FUNDS
This section talks about where the Secretary will get the money to cover the aforementioned grants. This includes primary funds from reimbursements and secondary funds from the previous award year. If there are insufficient funds, the total dollar amount in grants will be reduced.
420W - DEFINITIONS
This section defines terms like "value-added earnings" (student income), "geographic adjustment" (location of the institution), "earnings measurement period" (1, 2, or 4 years after program completion, depending on level of study), and "program length" (minimum amount of time specified in course guide). Per the aforementioned Act, an amendment is added to include reserve funds returned to the Secretary for the purpose of awarding PROMISE grants.
30051 - REGULATORY RELIEF
This section is in reference to the same Act, amending several references to "gainful employment" and discussing student hardship, including closed school discharge (when a school shutters before you graduate) and borrower defense repayment (if a school misled you or engaged in other misconduct or violation of state laws).
492A - LIMITATION ON AUTHORITY OF THE SECRETARY TO PROPOSE OR ISSUE REGULATIONS AND EXECUTIVE ACTIONS
This section gives the Secretary of Education authority to determine whether regulations or executive action should be passed or not, based on financial or adverse effect on the "economy, productivity, competitions, jobs, the environment, public health or safety, or state, local, or tribal governments and communities."
TITLE IV – ENERGY AND COMMERCE
41001 - RESCISSIONS RELATING TO CERTAIN INFLATION REDUCTION ACT PROGRAMS
This section pertains to Public Law 117-169 and states that the $200,000,000 appropriated to the Secretary in 2022 (then Jennifer Granholm) and committed to things like State-Based Home Energy Efficiency Contractor Training Grants, Department of Energy (DOE) loans, Energy Infrastructure Reinvestment Financing, Offshore Wind Electricity Transmission Planning, Modeling, and Analysis, and the Tribal Energy Loan Guarantee Program is rescinded.
41002 - NATURAL GAS EXPORTS AND IMPORTS
This portion amends Section 3 of the Natural Gas Act of 1938 to state that the Secretary (currently Chris Wright) can charge a $1,000,000 fee to foreign countries for application to export or import natural gas if there is not a free-trade agreement.
41003 - FUNDING FOR DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY LOAN GUARANTEE EXPENSES
This section states that in addition to available funds for the DOE, another $5,000,000 will be added for any expenses associated with "construct(ing) and operat(ing) a liquified natural gas project to transport liquified natural gas from...Alaska," as per Section 116 of the Alaskan Natural Gas Pipeline Act.
41004 - EXPEDITED PERMITTING
This section is in reference to the same Act and adds wording to define terms and how to submit an "expedited review," including paying the Secretary $10,000,000 or 1% of expected construction costs. Applications require a judicial review, where it will be determined whether the claim will cause "irreparable economic harm from approval" or not.
41005 - DE-RISKING COMPENSATION PROGRAM
This section states that in addition to available funds for the DOE (for fiscal year 2025), another $10,000,000 will be made available to compensate sponsors who "suffer unrecoverable losses due to qualifying Federal actions." Covered sponsors include those who work in extraction and transportation of coal and coal byproducts, oil, natural gas, and nuclear energy. These funds will be available until 2034.
41006 - STRATEGIC PETROLEUM RESERVE
This section states that in addition to available funds for the DOE (for fiscal year 2025), another $218,000,000 will be added for maintenance and repairs to Strategic Petroleum Reserve facilities and $1,321,000,000 will be added to purchase petroleum products. The previous Drawdown and Sale Mandate that allowed for sale of petroleum from U.S. reserves in order to regulate prices is repealed.
42101 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO CLEAN HEAVY-DUTY VEHICLES
Section 132 of the Clean Air Act, which had appropriated $1,000,000,000 for eligible contractors to be awarded for replacing large, low-efficiency vehicles, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42102 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO GRANTS TO REDUCE AIR POLLUTION AT PORTS
Section 133 of the Clean Air Act, which had appropriated $3,000,000,000 to purchase or install zero-emission port equipment or technology and award rebates to eligible contractors, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42103 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO GREENHOUSE GAS REDUCTION FUND
Section 134 of the Clean Air Act, which had appropriated $18,970,000,000 in grants and financial assistance for States, municipalities, and Tribal governments to deploy zero-emission technologies and carry out greenhouse gas emission reduction activities, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42104 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO DIESEL EMISSIONS
Section 60104 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $60,000,000 to identify and reduce diesel emissions "in low-income and disadvantaged communities," is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42105 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO FUNDING TO ADDRESS AIR POLLUTION
Section 60105 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $117,500,000 for fenceline air monitoring, screening air monitoring, national air toxics trend stations, and community monitoring, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42106 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO FUNDING TO ADDRESS AIR POLLUTION AT SCHOOLS
Section 60106 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $50,000,000 to monitor and reduce air pollutants at schools in low-income and disadvantaged communities, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42107 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO LOW EMISSIONS ELECTRICITY PROGRAM
Section 135 of the Clean Air Act, which had appropriated $87,000,000 for education and partnerships with consumers, low-income and disadvantaged communities, industries, and State, local, and Tribal governments in order to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42108 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO FUNDING FOR SECTION 211(O) OF THE CLEAN AIR ACT
Section 60108 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $15,000,000 for the development of tests and protocols regarding public health effects of fuel or fuel additives and the impacts of transportation fuel on low-income and disadvantaged communities, as well as investment in biofuels, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42109 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO FUNDING FOR IMPLEMENTATION OF THE AMERICAN INNOVATION AND MANUFACTURING ACT
Section 60109 of Public Law 117-169, as it relates to Division S of Public Law 116-260, which had appropriated $38,500,000 for the regulation of ozone-depleting compounds like hydrochlorofluorocarbons and toxic chemicals, as well as monitoring and reporting requirements, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42110 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO FUNDING FOR ENFORCEMENT TECHNOLOGY AND PUBLIC INFORMATION
Section 60110 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $25,000,000 for necessary information technology infrastructure for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), grants to States, tribes, and air pollution control agencies, and inspection software to be used by the EPA and aforementioned local governments, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42111 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO GREENHOUSE GAS CORPORATE REPORTING
Section 60111 of Public Law 117-169, which had appropriated $5,000,000 in order to enhance transparency of corporate climate action commitments and plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42112 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO ENVIRONMENTAL PRODUCT DECLARATION ASSISTANCE
Section 60112 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $250,000,000 to provide grants to businesses that manufacture products for verifying environmental declarations, for providing technical assistance to these businesses, and to carry out any other activities that assist in measuring, reporting, and reducing carbon construction materials, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42113 - REPEAL OF FUNDING FOR METHANE EMISSIONS AND WASTE REDUCTION INCENTIVE PROGRAM FOR PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS SYSTEMS
Section 136 of the Clean Air Act, which incentivized methane mitigation and monitoring with $850,000,000 in grants, rebates, contracts, and loans in order to provide financial and technical assistance to facility operators who comply with greenhouse gas reporting, and $700,000,000 for methane mitigation from conventional wells, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42114 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO GREENHOUSE GAS AIR POLLUTION PLANS AND IMPLEMENTATION GRANTS
Section 137 of the Clean Air Act, which appropriated $5,000,000,000 in grants to States, tribes, and local governments to implement measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42115 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY EFFICIENT, ACCURATE, AND TIMELY REVIEWS
Section 60115 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $40,000,000 to provide efficient, accurate, and timely reviews, hire and train personnel, and develop environmental data or information systems that include community engagement and purchase of equipment for environmental analysis, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42116 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO LOW-EMBODIED CARBON LABELING FOR CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
Section 60116 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $100,000,000 to identify and label materials used in road construction and for federal buildings that have fewer greenhouse gas emissions in all stages of production, use, and disposal, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42117 - REPEAL AND RESCISSION RELATING TO ENVIRONMENTAL AND CLIMATE JUSTICE BLOCK GRANTS
Section 138 of the Clean Air Act, which appropriated $3,000,000,000 to award grants for community-led pollution monitoring and prevention, using zero-emission technologies and infrastructure, and mitigating climate and health risks, including tribes, nonprofit organizations, and community partnerships, is repealed and all funds are rescinded.
42201 - REPEAL OF EPA RULES RELATING TO GREENHOUSE GAS AND MULTI-POLLUTANT EMISSIONS STANDARDS
All rules issued by the EPA relating to Later Model Year Light-Duty Vehicle (i.e. cars and trucks) Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards, as well as Multi-Pollutant Emissions Standards for newer models and medium-duty vehicles, will no longer have force or effect.
42301 - REPEAL OF NATIONAL HIGHWAY TRAFFIC SAFETY ADMINISTRATION (NHTSA) RULES RELATING TO CAFE STANDARDS
All rules issued by the NHTSA regarding Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards (how far you travel on a gallon of gas) for passenger cars and light trucks will no longer have force or effect.
Total financial loss for the environment: $33,308,000,000.
43101 - IDENTIFICATION AND AUCTION OF SPECTRUM
This section discusses the broadening of radio frequencies for federal and non-federal use, requiring not less than 600 megahertz of spectrum (full range of frequences and wavelengths of electromagnetic waves) for mobile broadband services. This will be auctioned off by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for licenses.
43201 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY MODERNIZATION INITIATIVE
As per the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020, the term "artificial intelligence" is defined as "a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations or decisions influencing real or virtual environments."
$500,000,000 will be appropriated for fiscal year 2025 to modernize federal information technology and deploy the use of artificial intelligence (AI) within the Department of Commerce. This includes replacing business systems and increasing efficiency and service delivery. No state or political subdivision may limit, restrict, or otherwise regulate any AI system or model entered into interstate commerce. This includes routing, zoning, procurement, or any procedure that facilitations the adoption of AI, and cannot impose civil liability, taxation, fees or other requirements on AI.
44101 - MORATORIUM ON IMPLEMENTATION OF RULE RELATING TO ELIGIBILITY AND ENROLLMENT IN MEDICARE SAVINGS PROGRAMS
The Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) (currently Robert F. Kennedy) cannot implement, administer, or enforce provisions of the final rule published by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services in September 2023, which simplified the process for individuals to enroll and retain eligibility in Medicare Savings Programs (MSPs), through 2035.
44102 - MORATORIUM ON IMPLEMENTATION OF RULES RELATING TO ELIGIBILITY AND ENROLLEMENT FOR MEDICAID, CHIP, AND THE BASIC HEALTH PROGRAM
The Secretary of HHS cannot implement, administer, or enforce the provisions of the final rule published by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services in April 2024, which simplified the enrollment process for Medicaid, the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and the Basic Health Program (BHP), and eliminated access barriers for children, through 2035.
44103 - ENSURING APPROPRIATE ADDRESS VERIFICATION UNDER THE MEDICAID AND CHIP PROGRAMS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is amended to add a process to "regularly obtain address information for individuals enrolled," and submit this information to the system "not less frequently than once each month" the social security number of each individual, and any other information "determined necessary" by the Secretary, so as to prevent enrolling in more than one state. $30,000,000 is allocated to create a system to prevent such multi-enrollments. Sources used for this system could include a forwarded address on a returned piece of mail, a Post Office change-of-address form, or a state health plan in another state. All State health plans that deliver care, inpatient or otherwise, must submit the home address of their patients to the State for verification. All the same actions will be taken with enrollees of the CHIP program.
44104 - MODIFYING CERTAIN STATE REQUIREMENTS FOR ENSURING DECEASED INDIVIDUALS DO NOT REMAIN ENROLLED
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is further amended, adding quarterly screenings and reviews of the Death Master File (a database run by the Social Security Administration) to determine if enrolled individuals are deceased. If so, the individual would be disenrolled and all payments would stop. However, if an error occurs and an individual is labeled "dead" who is indeed alive, they will be re-enrolled. The State has the ability to use any data sources to identify potentially deceased beneficiaries, and nothing should stop them from doing so.
44105 - MEDICAID PROVIDER SCREENING REQUIREMENTS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is further amended to state that Medicaid providers must be screened on a monthly bases to determine whether the Secretary has terminated their participation under title XVIII (Health Insurance for the Aged and Disabled) or child health plan under title XXI (Supplemental Security Income for the Aged, Blind, and Disabled).
44106 - ADDITIONAL MEDICAID PROVIDER SCREENING REQUIREMENTS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is further amended to include quarterly screenings against the Death Master File to make sure a provider or supplier is not deceased.
44107 - REMOVING GOOD FAITH WAIVER FOR PAYMENT REDUCTION RELATED TO CERTAIN ERRONEOUS EXCESS PAYMENTS UNDER MEDICAID
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act is amended to remove the good faith option, which allowed states to demonstrate good faith efforts to manage their eligibility error rate, still giving them an allowance of federal funds.
44108 - INCREASING FREQUENCY OF ELIGIBILITY REDETERMINATIONS FOR CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is amended to require redetermination of eligibility every six months.
44109 - REVISING HOME EQUITY LIMIT FOR DETERMINING ELIGIBILITY FOR LONG-TERM CARE SERVICES UNDER THE MEDICAID PROGRAM
Section 1917 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that the prior maximum home equity interest limit of $1,097,000 required for long-term care eligibility, that grew annually based on inflation, will now cap out at $1,000,000 with no growth over time. There will no longer be exceptions for the elderly, blind, or disabled.
44110 - PROHIBITING FEDERAL FINANCIAL PARTICIPATION UNDER MEDICAID AND CHIP FOR INDIVIDUALS WITHOUT VERIFIED CITIZENSHIP, NATIONALITY, OR SATISFACTORY IMMIGRATION STATUS
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that no Medicaid or CHIP federal funds will be used toward individuals without "satisfactory immigrant status," for which they will be given 90 days to prove their position of legal residency. A state may choose to provide care during this timeframe, but federal funds will not be available until they can prove their status.
44111 - REDUCING EXPANSION FMAP FOR CERTAIN STATES PROVIDING PAYMENTS FOR HEALTHCARE FURNISHED TO CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Section 1905 of the Social Security Act is amended to change the Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) from 90% to 80% for states that provide Medicaid coverage to undocumented immigrants.
44121 - MORATORIUM ON IMPLEMENTATION OF RULE RELATING TO STAFFING STANDARDS FOR LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES UNDER THE MEDICARE AND MEDICAID PROGRAMS
The Secretary of HHS cannot implement, administer, or enforce the provisions of the final rule published by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid, which established minimum staffing standards for long-term care facilities in order to ensure safe and quality care.
44122 - MODIFYING RETROACTIVE COVERAGE UNDER THE MEDICAID AND CHIP PROGRAMS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that eligible applicants for Medicaid and Chip will no longer receive three-month retroactive coverage for care, but instead just one month.
44123 - ENSURING ACCURATE PAYMENTS TO PHARMACIES UNDER MEDICAID
Section 1927 of the Social Security Act is amended to require pharmacies to be transparent about acquisition costs, whether retail or non-retail, in order to determine a national cost benchmark (including discounts, rebates, and other price concessions) so as to establish more consistent Medicaid reimbursement rates. $13,000,000 will be appropriated to DHHS for periodic studies of survey data.
44124 - PREVENTING THE USE OF ABUSIVE SPREAD PRICING IN MEDICAID
Section 1927 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that there will be a contract between the State and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) that will allow for more oversight in order to prevent "abusive spread pricing" (when BPMs charge Medicaid more for the same drug), and require a "pass-through pricing model" which would limit what BPMs can charge for pharmaceuticals.
44125 - PROHIBITING FEDEARL MEDICAID AND CHIP FUNDING FOR GENDER TRANSITION PROCEDURES
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act is amended to disallow federal funding from Medicaid or CHIP to be used to cover gender-affirming hormone therapy and surgeries, and puberty blockers for minors. This includes a very long and specific list of surgeries, including cosmetic, meant to "feminize or masculinize the facial or other body features of an individual." However, puberty blockers can be prescribed to individuals experiencing precocious (early) puberty, and treatments can be prescribed for individuals born with both sexes.
44126 - FEDERAL PAYMENTS TO PROHIBITED ENTITIES
No federal funds under title XIX (Medicaid) can be used for "prohibited entities." This includes abortion providers, non-profit essential community providers that are engaged in family planning and reproductive health, and 501(c)(3) tax-exempt organizations.
44131 - SUNSETTING ELIGIBILITY FOR INCREASED FMAP FOR NEW EXPANSION STATES
Section 1905 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that the temporary 5% enhanced Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) given to states under the American Rescue Plan Act will be rescinded.
44132 - MORATORIUM ON NEW OR INCREASED PROVIDER TAXES
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act is amended to freeze existing state provider tax rates in order to prevent increased rates with new providers.
44133 - REVISING PAYMENTS FOR CERTAIN STATE DIRECTED PAYMENTS
The Secretary of HHS will allow for upper payment limit increases for non-expansion states (those that have chosen not to expand their Medicaid programs to cover individuals with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level).
44134 - REQUIREMENTS REGARDING WAIVER OF UNIFORM TAX REQUIREMENT FOR MEDICAID PROVIDER TAX
Section 1903 of the Social Security Act is amended to prevent states from using non-uniform provider taxes (taxing healthcare providers in order to cover Medicaid fees) that would send costs back to the federal government.
44135 - REQUIRING BUDGET NEUTRALITY FOR MEDICAID DEMONSTRATION PROJECTS UNDER SECTION 1115
Section 1115 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that the Secretary may not approve an application of a Medicaid demonstration project, which allows states to try new approaches to providing Medicaid services, if it isn't fiscally responsible.
44141 - REQUIREMENT FOR STATES TO ESTABLISH MEDICAID COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT REQUIREMENTS FOR CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that all eligible applicants for assistance must show community engagement, including working 80 hours/month, being enrolled in school at least half-time, or has a monthly income not less than the minimum wage requirement. Exceptions include pregnancy or incarceration.
44142 - MODIFYING COST SHARING REQUIREMENTS FOR CERTAIN EXPANSION INDIVIDUALS UNDER THE MEDICAID PROGRAM
Section 1916 of the Social Security Act is amended to state that individuals making a certain percentage over the federal poverty line would be required to pay a portion of their medical costs. This cannot exceed 5% of the total family income.
44201 - ADDRESSING WASTE, FRAUD, AND ABUSE IN THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT (ACA) EXCHANGES
Section 1311 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act is amended to require more rigorous income verification, disallowing for self-attested income (to the best of your knowledge), which could be cross-checked with other government databases. It will also shorten the open enrollment period from 2.5 months to 1.5 months, beginning November 1st and ending December 15th. Special enrollment periods for those at 100% and higher of the Federal Poverty Level would be eliminated. Gender-affirming care procedures as an "essential health benefit" would also be eliminated.
44202 - FUNDING COST SHARING REDUCTION (CSR) PAYMENTS
Section 1402 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act is amended to appropriate funds for reimbursement to private health plans that offer CSRs. CSR payments cannot be made to insurers offering plans to cover abortion services, except in cases of rape, incest, or to save a mother's life.
44301 - EXPANDING AND CLARIFYING THE EXCLUSION FOR ORPHAN DRUGS UNDER THE DRUG PRICE NEGOTIATION PROGRAM
Section 1192 of the Social Security Act is amended to expand the exclusion of orphan drugs (commercially undeveloped because it won't make the pharmaceutical companies much money) of single rare diseases from price negotiations, to drugs that treat more than one disease. These drugs need to be on the market longer and go through more research and development before prices can be negotiated.
44302 - STREAMLINED ENROLLMENT PROCESS FOR ELIGIBLE OUT-OF-STATE PROVIDERS UNDER MEDICAID AND CHIP
Section 1902 of the Social Security Act is amended to allow eligible out-of-State providers to enroll under the State Medicaid and CHIP plans, so as to streamline the process for pediatric patients who cross state lines for increased access to complex care.
44303 - DELAYING DSH REDUCTIONS
Section 1923 of the Social Security Act is amended to push back the intended Disproportionate Share Hospital (DSH) reductions (supplemental payments made to hospitals that treat more-than-the-normal amount of low-income patients who are often uninsured or covered by Medicaid) from 2026-2028 to 2029-2031.
44304 - MODIFYING UPDATE TO THE CONVERSATION FACTOR UNDER THE PHYSICIAN FEE SCHEDULE UNDER THE MEDICARE PROGRAM
Section 1848 of the Social Security Act is amended to change the Medicare Conversion Factor (CF) (determines how much providers are paid from Medicare payments) to better reflect increases in inflation and costs.
44305 - MODERNIZING AND ENSURING PHARMACY BENEFIT MANAGER (PBM) ACCOUNTABILITY
Section 1860 of the Social Security Act is amended to require transparency from PBMs via cost-performance evaluations, in order to prevent over-earnings from drug list prices, rather than bona fide service fees (i.e. they don't earn based on the rate of drug-cost increases, but the work they do behind the counter).
TITLE V -- COMMITTEE ON FINANCIAL SERVICES
50001 GREEN AND RESILIENT RETROFIT PROGRAM FOR MULTIFAMILY FAMILY HOUSING
The unused balance of $5,000,000,000 appropriated in Public Law 117-169, commonly known as the "Inflation Reduction Act, meant for improving energy and water efficiency, enhancing indoor air quality, implementing the use of zero-emission electricity generation, and addressing climate resilience in affordable housing, is rescinded.
50002 - PUBLIC COMPANY ACCOUNTING OVERSIGHT BOARD
All information previously collected by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), a non-profit created to oversee audits of U.S.-listed companies, will be transferred over to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), a federal agency. All rights and roles of the PCAOB will be transferred to the SEC, and any remaining funds will be deposited into the U.S. Treasury.
50003 - BUREAU OF CONSUMER FINANCIAL PROTECTION
Section 1017 of the Consumer Financial Protection Act of 2010, commonly known as the "Dodd-Frank Act," is amended to state that there will be a reduction in the maximum amount of money that the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) can request every year from the Federal Reserve, and that the CFPB must return any unobligated (unused) money back to the Treasury.

50004 - CONSUMER FINANCIAL CIVIL PENALTY FUND
Normally the CFPB will take legal action against a company that breaks the law, requiring them to pay into the Civil Penalty Fund, which is pooled to compensate victims across multiple cases. Section 1017 of the Consumer Financial Protection Act of 2010 will amended this rule, limiting who can receive these funds. The funds can also no longer be used for consumer education and financial literacy.
50005 - FINANCIAL RESEARCH FUND
Section 155 of the Financial Stability Act of 2010 is amended to state that there will be a limit on the assessments on large banks made by the Office of Financial Research (OFR) and the Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC), and that excess funds will be transferred into the Treasury.
TITLE VI -- COMMITTEE ON HOMELAND SECURITY
60001 - BORDER BARRIER SYSTEM CONSTRUCTION, INVASIVE SPECIES, AND BORDER SECURITY FACILITIES IMPROVEMENTS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $46,500,000,000 will be added for barrier systems, lights, sensors, and other detection technology, $50,000,000 for removing invasive species that impede border security operations, and $5,000,000,000 to lease and buy land, and build facilities and checkpoints.
60002 - U.S. CUSTOMS AND BORDER PROTECTION PERSONNEL AND FLEET VEHICLES
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $4,100,000,000 will be added to hire and train Border Patrol personnel, $2,052,630,000 for signing and retention bonuses, $813,000,000 for marked patrol vehicles, $285,000,000 for training Federal law enforcement personnel, $465,000,000 to buy land and build training centers, and $600,000,000 for marketing to, recruiting, and vetting border security applicants.
60003 - U.S. CUSTOMS AND BORDER PROTECTION TECHNOLOGY, NATIONAL VETTING CENTER, AND OTHER EFFORTS TO ENHANCE BORDER SECURITY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $1,076,317,000 will be added to buy equipment, artificial intelligence (AI), and other mission support to combat illicit narcotics, $2,766,000,000 for upgrades and border surveillance, $673,000,000 for technology related to biometric entry and exit system(s) (facial recognition, fingerprinting), $1,234,000,000 for upgrades to rapid air and marine response,$16,000,000 for screening and background checks, $500,000,000 for enhancing border security, and $1,000,000 for commemorating efforts and events at the border (rewarding agents for a "job well done").
60004 - STATE AND LOCAL LAW ENFORCEMENT PRESIDENTIAL RESIDENCE PROTECTION
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $300,000,000 will be added for law enforcement personnel costs and protection activities related to the residence of the President.
60005 - STATE HOMELAND SECURITY GRANT PROGRAM
In addition to already appropriated funds, an additional $500,000,000 will be added to detect and monitor unmanned aircraft (drones), $625,000,000 for security and other costs related to the 2026 FIFA World Cup, $1,000,000,000 for security and other costs related to the 2028 Olympics, and $450,000,000 for the Operation Stonegarden Grant Program, which helps state, local, and tribal communities improve border security.
Total spending for this portion of H.R. 1 is $69,006,947,000
TITLE VII -- COMMITTEE ON THE JUDICIARY
70001 - APPLICABILITY OF THE IMMIGRATION LAWS
This section states that regardless of any rules written into immigration laws, all fees under this subtitle still apply.
70002 - ASYLUM FEE
This section states that all asylum-seekers must pay a $1000 application fee. This is an increase from $600 for large employers and $300 for small employers that went into effect on April 1, 2024. Prior to that there was no fee. This fee cannot be waived or reduced.
70003 - EMPLOYMENT AUTHORIZATION DOCUMENT FEES
This section states that all immigrants applying for employment authorization must pay an additional $550 application fee, including those on parole in the U.S. and those granted Temporary Protected Status (TPS), or whose country of origin is too unsafe to return. This fee cannot be waived or reduced.
70004 - PAROLE FEE
This section states that all immigrants paroled in the U.S. for "case-by-case" limitations must pay an additional $1000 fee. This fee cannot be waived or reduced.
70005 - SPECIAL IMMIGRANT JUVENILE FEE
This section states that all immigrants applying for Special Immigrant Juvenile (SIJ) status--who are under 21 and unmarried--must pay a $500 fee for reunification with a parent or legal guardian. Note: the wording has changed from "You cannot be reunified with one or both of your parents because of...abuse, abandonment, neglect" to "reunification is viable, notwithstanding abuse, neglect, (or) abandonment." This fee cannot be waived or reduced.
70006 - TEMPORARY PROTECTED STATUS FEE
This section states that all immigrants applying for TPS who have overstayed their visa must pay a $500 fee. This fee cannot be waived or reduced.
70007 - UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILD SPONSOR FEE
This section requires sponsors of "unaccompanied alien children (UACs)" to pay an unspecified amount up front for processing, housing, feeding, educating, transporting, and otherwise caring for the child, before the child can be released to the sponsor.
70008 - VISA INTEGRITY FEE
This section requires immigrants traveling to the U.S. pursuant to a nonimmigrant visa (i.e. foreign nationals visiting the U.S. for business, tourism, or study) to pay a $250 fee. This fee may be reimbursed if the applicant complies with the "period of authorized stay" or provides a valid reason for extending the nonimmigrant visa.
70009 - FORM I-94 FEE
This section requires anyone filling out an I-94 form, which serves as a record of admission to the U.S. including length of stay, to pay a $30 fee, up from the current $6 fee.
70010 - YEARLY ASYLUM FEE
This section requires an immigrant to pay $100 every year while their asylum application is pending.
70011 - FEE FOR CONTINUANCES GRANTED IN IMMIGRATION COURT PROCEEDINGS
This section requires any immigrant who is granted a continuance (postponement) in immigration court to pay a $100 fee.
70012 - FEE RELATING TO RENEWAL AND EXTENSION OF EMPLOYMENT AUTHORIZATION FOR PAROLEES
This section requires any immigrant paroled in the U.S. who wants to renew or extend his or her employment authorization to pay a fee of $550 every six months.
70013 - FEE RELATING TO TERMINATION, RENEWAL, AND EXTENSION OF EMPLOYMENT AUTHORIZATION FOR ASYLUM APPLICANTS
This section requires any asylum applicant who wants to renew or extend their employment authorization to pay a fee of $550 every six months. Any employment authorization will be terminated if an asylum application is denied.
70014 - FEE RELATING TO RENEWAL AND EXTENSION OF EMPOYMENT AUTHORIZATION FOR ALIENS GRANTED TEMPORARY PROTECTED STATUS
This section requires any immigrant who is granted TPS and wants to renew or extend their employment authorization to pay a $550 fee every six months.
70015 - DIVERSITY IMMIGRANT VISA FEES
This section requires any applicant who is selected through the diversity visa or "green card lottery" to pay a $250 fee to be included in the lottery, and another $400 if chosen, to pay for the visa. Previously there was no fee to be included in the lottery, and a $330 diversity visa fee if chosen.
70016 - EXECUTIVE OFFICE FOR IMMIGRATION REVIEW (EOIR) FEES
This section requires any immigrant applying for adjustment of status--transitioning from a nonimmigrant visa to a green card--to pay a $1500 fee. An immigrant applying for a Wavier of Grounds of Inadmissibility, or appealing a denial for health issues or possible criminal history, will have to pay $1050 to be adjudicated by an immigration judge. An immigrant filing for Temporary Protected Status (TPS) due to a lack of safety in their country of origin will have to pay a $500 fee. Any immigrant appealing a visa denial will have to pay $900 to meet with a judge, as will anyone appealing a denial from DHS. If someone is in the process of appealing allegations of misconduct, including censure or suspension of a license, they will pay $1325. Filing a motion to reopen or reconsider a decision will cost $900. An appeal or request for extension of a deportation order is $600. An application to "cancel the removal of a permanent resident" is also $600, and for nonpermanent residents it's $1500.
70017 - ELECTRONIC SYSTEM FOR TRAVEL AUTHORIZATION (ESTA) FEE
This section raises the fee to use the ESTA, which is required for travel to the U.S., from $21 to $40
70018 - IMMIGRATION USER FEES
This section raises the immigration user fees by air, land, and sea from $7 to $10.
70019 - ELECTRONIC VISA UPDATE SYSTEM (EVUS) FEE
The EVUS system allows immigrants traveling to the U.S. to update their biographical and travel information via a publicly-accessible website. It must be updated at least every two years, and will cost $30 to enroll. Currently there is no fee.
70020 - FEE FOR SPONSOR OF UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILD WHO FAILS TO APPEAR IN IMMIGRATION COURT
This section requires a sponsor of an unaccompanied child to pay a $5000 fee before the child will be released to them.
70021 - FEE FOR ALIENS ORDERED REMOVED IN ABSENTIA
This section requires an immigrant removed in absentia, or ordered to be deported prior to their final hearing and arrested by ICE, to pay a $5000 fee.
70022 - CUSTOMS AND BORDER PROTECTION INADMISSIBLE ALIEN APPREHENSION FEE
If an immigrant is considered "inadmissible," whether for health reasons or criminal background, they will be charged $5000 for entering the U.S. and being apprehended by Customs and Border Protection.
70023 - AMENDMENT TO AUTHORITY TO APPLY FOR ASYLUM
This section amends the Immigration and Nationality Act, which governs immigration in the U.S., to require the Attorney General to charge fees for seeking asylum and applying for employment authorization, and to remove limitations on fees.
70100 - EXECUTIVE OFFICE FOR IMMIGRAITON REVIEW
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $1,250,000,000 will be added to the EOIR for hiring support staff and immigration judges, and building bigger courtrooms.
70101 - ADULT ALIEN DETENTION CAPACITY AND FAMILY RESIDENTIAL CENTERS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $45,000,000,000 will be provided to ICE to build detention facilities for individuals and families. These facilities can house children, whether or not they are licensed by the state in which they reside. In order to spend funding efficiently, DHS has the authority to set detention standards (i.e. quality of environment, food, space, etc.).
70102 - RETENTION AND SIGNING BONUSES FOR U.S. IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT PERSONNEL
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $858,000,000 will be given in the form of $10,000 hiring and retention bonuses for ICE personnel.
70103 - HIRING OF ADDITIONAL U.S. IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT PERSONNEL
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $8,000,000,000 will be given to ICE personnel to carry out immigration enforcement.
70104 - U.S. IMMIGRATION AND CUSTOMS ENFORCEMENT HIRING CAPABILITY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $600,000,000 will be given to ICE for recruitment, hiring, onboarding, and to carry out immigration enforcement.
70105 - TRANSPORTATION AND REMOVAL OPERATIONS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $14,400,000,000 will be given to ICE for transportation, including escorted commercial flights and transportation of unaccompanied immigrant children.
70106 - INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INVESTMENTS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $700,000,000 will be given to ICE for technology used in enforcement and removal of undocumented immigrants.
70107 - FACILITIES UPGRADES
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $550,000,000 will be given to ICE for facility upgrades used for enforcement and removal of undocumented immigrants.
70108 - FLEET MODERNIZATION
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $250,000,000 will be given to ICE for upgrades to vehicles and aircraft used for transportation and removal of undocumented immigrants.
70109 - PROMOTING FAMILY UNITY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $20,000,000 will be given to DHS to fund a short-term detention space where undocumented immigrants can be detained with their children.
70110 - FUNDING SECTION 287(G) OF THE IMMIGRATION AND NATIONALITY ACT (INA)
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $650,000,000 will be given to ICE to implement section 287(g) of the INA, which allows state and local law enforcement to detain and remove undocumented immigrants.
70111 - COMPENSATION FOR INCARCERATION OF CRIMINAL ALIENS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $950,000,000 will be allocated to create a program similar to the State Criminal Alien Assistance Program (SCAAP), which reimburses states and localities for incarcerating undocumented immigrants.
70112 - OFFICE OF THE PRINCIPAL LEGAL ADVISOR
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $1,320,000,000 will be given to the Office of the Principal Legal Advisor, which represents DHS in immigration-removal court cases, in order to hire more attorneys and support staff.
70113 - RETURN OF ALIENS ARRIVING FROM CONTIGUOUS TERRITORY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $500,000,000 will be given to DHS to cover the costs of returning undocumented immigrants to their countries of origin.
70114 - STATE AND LOCAL PARTICIPATION IN HOMELAND SECURITY EFFORTS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $787,000,000 will be given to ICE to end the presence of gangs and international criminal organizations in the U.S.
70115 - UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILDREN CAPACITY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $3,000,000,000 will be used to fund the Office of Refugee Resettlement--meant to offer support for refugees seeking safe haven in the U.S.--to house, transport, and supervise unaccompanied children.
70116 - DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY CRIMINAL AND GANG CHECKS FOR UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILDREN
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $20,000,000 will be given to DHS to check unaccompanied minors ages 12 and over for gang-affiliated tattoos and to determine if they have a criminal history.
70117 - DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES (DHHS) CRIMINAL AND GANG CHECKS FOR UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILDREN
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $20,000,000 will be given to DHHS to check unaccompanied minors ages 12 and over for gang-affiliated tattoos and to determine if they have a criminal history.
70118 - INFORMATION ABOUT SPONSORS AND ADULT RESIDENTS OF SPONSOR HOUSEHOLDS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $50,000,000 will be given to DHHS to provide information to DHS regarding an unaccompanied minor's home situation before being released to a sponsor. This includes names, social security numbers, birthdates, immigration status, contact info, and background and criminal records, including checking the sex-offender registry and fingerprinting.
70119 - REPATRIATION OF UNACCOMPANIED ALIEN CHILDREN
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $100,000,000 will be given to DHS to allow unaccompanied migrant children to withdraw their applications of admission if they are not victims of "severe" forms of trafficking or afraid to return to their countries of origin.
70120 - U.S. SECRET SERVICES
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $1,170,000,000 will be given to the Secret Service for protection and security operations.
70121 - COMBATING DRUG TRAFFICKING AND ILLEGAL DRUG USE
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $500,000,000 will be given to the Department of Justice (DOJ) to combat drug trafficking and illegal drug use.
70122 - INVESTIGATING AND PROSECUTING IMMIGRATION RELATED MATTERS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $600,000,000 will be given to the DOJ to prosecute immigration-related crimes, including voting and applying for welfare.
70123 - EXPEDITED REMOVAL FOR CRIMINAL ALIENS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $75,000,000 will be given to DHS to expedite removal proceedings for undocumented immigrants.
70124 - REMOVAL OF CERTAIN CRIMINAL ALIENS WITHOUT FURTHER HEARING
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $25,000,000 will be given to DHS to streamline court proceedings to remove undocumented immigrants suspected of being inadmissible for security reasons.
70200 - REVIEW OF AGENCY RULEMAKING
In addition to already-appropriated funds, an additional $10,000,000 each will be given to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Comptroller General of the U.S. to increase activities related to rulemaking, and require Congress to approve rules that increase revenue before they go into effect.
70300 - LIMITATION ON DONATIONS MADE PURSUANT TO SETTLEMENT AGREEMENTS TO WHICH THE UNITED STATES IS A PARTY
This section prohibits the DOJ from being involved in a settlement agreement where the settling party pays funds to a third party for anything other than restitution.
70301 - SOLICITATION OF ORDERS DEFINED
Section 101(d) of Public Law 86-272 is amended to define "solicitation of orders" as any business activity meant for solicitation of orders--seeking goods or services--even if that activity has a separate valuable business function, clarifying tax treatment of these activities.
70302 - RESTRICTION ON ENFORCEMENT
This section clarifies that "judges wouldn't be able to issue contempt orders against defendants who defy the courts unless the person who first sued for an injunction"--a court order telling a person to do something, or stop doing something--"or restraining order had forked over a bond at the very start of their lawsuit." -- the Huffington Post
Total spending on immigration enforcement is $81,405,000,000
TITLE VIII -- COMMITTEE ON NATURAL RESOURCES
80101 - ONSHORE OIL AND GAS LEASE SALES
Section 17 of the Mineral Leasing Act is amended to state that onshore oil and gas lease sales on federal lands are to resume immediately (which were paused during the Biden Administration). This includes a minimum of four oil and gas lease sales in nine states and "any other state...available for oil and gas leasing."
80102 - NONCOMPETITIVE LEASING
Section 17 of the Mineral Leasing Act is further amended to state that any land that either is not bid on, or receives a low bid, will be offered up for non-competitive leasing (an agreement without a formal, competitive bidding process) within 30 days.
80103 - PERMIT FEES
Section 17 of the Mineral Leasing Act is further amended to state that two energy production sources that commingle will be treated as a single entity, but must pay an application fee of $10,000 and agree to install measurement devices for each energy source. For a single-lease permit it is $5000.
80104 - PERMITTING FEE FOR NON-FEDERAL LAND
This section states that the Secretary of the Interior (currently Doug Burgum) won't require a permit to drill for oil or gas if the leaseholder pays $5000 and isn't drilling on federal land.
80105 - REINSTATE REASONABLE ROYALTY RATES
Section 8 of the Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act is amended to reduce the current royalty rate of 16.67% (set by the Inflation Reduction Act in 2022) to 12.5% for new onshore and offshore gas and oil leases. (Royalties are earned by landowners who own the mineral rights beneath their property.)
80111 - GEOTHERMAL LEASING
Section 4 of the Geothermal Steam Act of 1970 is amended to hold annual (instead of biennial) geothermal lease sales, and replace those that are cancelled.
80112 - GEOTHERMAL ROYALTIES
Section 5 of the Geothermal Steam Act of 1970 is amended to state that more than one geothermal facility listed on the same lease will be treated as a separate entity when it comes to royalty payments.
80121 - COASTAL PLAIN OIL AND GAS LEASING
The administration will withdraw the 2024 Notice of Availability of the Record of Decision for the Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement for the Coastal Plain Oil and Gas Leasing Program, Alaska and reinstate the 2019 version, which would approve oil and gas leasing in the Coastal Plain of the Artic National Wildlife Refuge.
80141 - COAL LEASING
The Secretary will hold a lease sale within 90 days of enactment of this bill, and take all actions necessary to grant qualified applications. This includes making available for lease an additional 4,000,000 acres on Federal land.
80142 - FUTURE COAL LEASING
Secretarial Order 3338, instated by President Obama, which directed the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) to conduct a comprehensive review of the federal coal program, will no longer hold any weight.
80143 - COAL ROYALTY
Section 7 of the Mineral Leasing Act is amended to decrease the royalty rate from 12.5% to 7%.
80144 - AUTHORIZATION TO MINE FEDERAL MINERALS
All federal coal reserves leased under Federal Coal Lease MTM 97988 are authorized to be mined in accordance with the Bull Mountains (Montana) Mining Plan Modification, which was approved on June 6, 2025.
80151 - PROJECT SPONSOR OPT-IN FEES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEWS
The National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 is amended to state that project sponsors can pay for an environmental review, and if they do, an administrative and/or judicial review will no longer be necessary.
80152 - RESCISSION RELATING TO ENVIRONMENTAL AND CLIMATE DATA COLLECTION
Section 60401 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $32,500,000 to support data collection related to negative environmental harms and climate impacts, pollution, and temperature rise, is rescinded.
80161 - PROTEST FEES
Section 17 of the Mineral Leasing Act is amended to state that anyone protesting oil and gas lease sales must pay a filing fee of at least $150.
80171 - MANDATORY OFFSHORE OIL AND GAS LEASE SALES
This section states that there will be no fewer than 30 lease sales in the "Gulf of America" for 15 years after the enactment of this bill, and for not fewer than 80,000,000 acres. The Cook Inlet Planning Area in Alaska will hold no fewer than 6 sales, and for not fewer than 1,000,000 acres.
80172 - OFFSHORE COMMINGLING
The Secretary will approve commingling of drilling operators, unless it isn't safe or there is less production of gas and oil.
80173 - LIMITATIONS ON AMOUNT OF DISTRIBUTED QUALIFED OUTER CONTINENTAL SHELF REVENUES
Section 105 of the Gulf of Mexico Energy Security Act of 2006 is amended to raise the cap on Outer Continental Shelf (seabed belonging to the U.S.) revenues from $500,000,000 to $650,000,000.
80181 - RENEWABLE ENERGY FEES ON FEDERAL LANDS
On January 1st every year the Secretary will collect rent from holders of wind and solar energy projects, until those project begin to produce. Wind projects will see double the rent due to encumbrance (claim on a property), while solar will remain relatively steady.
80182 - RENEWABLE ENERGY REVENUE SHARING
Beginning January 1, 2026, money collected from renewable energy projects (wind, solar) on public land and National Forests will be deposited into the U.S. Treasury.
80201 - RESCISSION OF FUNDS FOR INVESTING IN COASTAL COMMUNITIES AND CLIMATE RESILIENCE
Section 40001 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $2,600,000,000 to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to tribes, non-profits, and schools for the protection of coastal and marine habitats, is rescinded.
80202 - RESCISSION OF FUNDS FOR FACILITIES OF NOAA AND NATIONAL MARINE SANCTUARIES
Section 40002 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $200,000,000 to NOAA to replace and repair piers and fisheries laboratories, and construct facilities to support the National Marine Sanctuary System (17 marine protected areas), is rescinded.
80202 - SURFACE WATER STORAGE ENHANCEMENT
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $2,000,000,000 will be added to increase the capacity of Bureau of Reclamation (responsible for hydroelectric power generation) surface-water storage facilities.
80204 - WATER CONVEYANCE ENHANCEMENT
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $500,000,000 will be added to increase Bureau of Reclamation conveyance facilities (pipelines, aqueducts, and canals).
80301 - RESCISSION OF FOREST SERVICE FUNDS
Section 23001 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $2,150,000,000 for fuel reduction (cutting back dead trees), brush removal, and protection of old-growth forests on the National Forest System, is rescinded.
80302 - RESCISSION OF NATIONAL PARK SERVICE (NPS) AND BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT (BLM) FUNDS
Section 50221 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $250,000,000 to carry out conservation and protection of lands and resources for NPS and BLM, is rescinded.
80303 - RESCISSION OF BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT (BLM) AND NATIONAL PARK SERVICE (NPS) FUNDS
Section 50222 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $250,000,000 to carry out conservation and ecosystem and habitat restoration on lands run by the NPS and BLM, is rescinded.
80304 - RESCISSION OF NATIONAL PARK SERVICE FUNDS
Section 50223 of Public Law 117-169, which appropriated $500,000,000 to the NPS for hiring employees, is rescinded.

80305 - CELEBRATING AMERICA'S 250TH ANNIVERSARY
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $190,000,000 will be added for events and celebrations relating to the 250th anniversary of the founding of the United States. The money would also be used to build a park known as the "National Garden of American Heroes," complete with statues of Founding Fathers, political figures, athletes, celebrities, and pop-culture icons.
80306 - LONG-TERM CONTRACTS FOR THE FOREST SERVICE
The Chief of the Forest Service will not enter into less than one long-term contract with public or private entities between now and 2034, and the funds will be deposited into the U.S. Treasury.
80307 - LONG-TERM CONTRACTS FOR THE BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT
The Director of BLM will not enter into less than one long-term contract with public or private entities between now and 2034, and the funds will be deposited into the U.S. Treasury.
80308 - TIMBER PRODUCTION FOR THE FOREST SERVICE
Within one year of the passage of this bill, the Secretary of Agriculture (currently Brooke Rollins) will increase the timber harvest on National Forest System lands by 25%.
80309 - TIMBER PRODUCTION FOR THE BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT
Within one year of the passage of this bill, the Secretary of the Interior will increase the timber harvest on public lands by 25%.
TITLE IX -- COMMITTEE ON OVERSIGHT AND GOVERNMENT REFORM
90001 - ELIMINATION OF THE FERS ANNUITY SUPPLEMENT FOR CERTAIN EMPLOYEES
Title 5 of the United States Code is amended to state that the FERS Annuity Supplement (also known as the Special Retirement Supplement (SRS)), which bridged the gap between federal workers retiring at age 62 and receiving Social Security benefits at age 67, will be eliminated as of January 1, 2028.
90002 - ELECTION FOR AT-WILL EMPLOYMENT AND LOWER FERS CONTRIBUTIONS FOR NEW FEDERAL CIVIL SERVICE HIRES
Title 5 of the United States Code is also amended to state that new federal employees can choose "at-will" employment (can be fired at any time without reason), allowing for a lower financial contribution to their Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS), and a higher contribution from their employer.
90003 - FILING FEE FOR MERIT SYSTEMS PROTECTION BOARD CLAIMS AND APPEALS
Title 5 of the United States Code is also amended to state that any employee, former employee, or applicant for employment filing a claim with the Merit Systems Protection Board (MSPB) (an independent agency that protects the rights of federal employees) will have to pay $350. Previously there was no fee.
90004 - FEDERAL EMPLOYEES HEALTH BENEFITS (FEHB) PROTECTION
This section makes significant changes to FEHB protections, including tightening verification requirements, changing the length of time the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) can retain records, auditing family members for fraud risk, and disenrolling "ineligible" participants. In addition to already-appropriated funds, $553,267,927 will be added to conduct audits of enrollment and eligibility.
TITLE X - COMMITTEE ON TRANSPORTATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE
100001 - COAST GUARD ASSETS NECESSARY TO SECURE THE MARITIME BORDER AND INTERDICT MIGRANTS AND DRUGS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $21,207,000,000 will be added for training, equipment, long-range unmanned aircraft systems, cutters (boats), and shoreside infrastructure. These funds can also be used by an "entity other than the Coast Guard" for acquisition, procurement (purchasing), and construction.
100002 - VESSEL TONNAGE DUTIES
Title 46 of the United States Code is amended to remove the tax-per-ton rate of 2 cents "not to exceed" 10 cents, and raising it to 4.5 cents "not to exceed" 22.5 cents.
100003 - REGISTRATION FEE ON MOTOR VEHICLES
Title 23 of the United States Code is amended to state that all electric vehicle owners will pay an annual $250 registration fee, and all hybrid vehicle owners will pay a $100 registration fee in addition to yearly state registration fees.
100004 - DEPOSIT OF REGISTRATION FEE ON MOTOR VEHICLES
Any money accrued from the previous section will be deposited into the Highway Trust Fund, which is used to finance highway and mass transit projects.
100005 - MOTOR CARRIER DATA
$500,000,000 will be appropriated to the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), an agency that regulates the trucking industry, to create a public website with data on motor carriers (businesses that transport goods or passengers across state lines), in order to show whether or not that carrier meets FMCSA requirements. A $100 fee will be charged for access to the website.
100006 - IRA RESCISSIONS
Funding for the Alternative Fuel and Low-Emission Aviation Technology Program, created by the Inflation Reduction Act to produce, transport, blend, and store sustainable aviation fuels and low-emission technologies, is permanently rescinded.
Funding for the Neighborhood Access and Equity Grant Program, which removed, replaced, or retrofitted highways and freeways in disadvantaged communities, is permanently rescinded.
Funding for Federal Building Assistance, which can include things like affordable housing, preservation and rehabilitation of low-income rental housing, healthcare facilities in rural areas, and Section 8 housing, is permanently rescinded.
Funding for Use of Low-Carbon Materials for Federal Building Assistance, included in the Inflation Reduction Act and FEMA'S Hazard Mitigation Assistance program, is permanently rescinded.
Funding for General Services Administration Emerging Technologies, which identifies new technologies that significantly impact the federal government, such as AI and blockchain, is permanently rescinded.
Any Environmental Review Implementation Funds, used to increase building capacity for local governments and tribes, as well as identify potential environmental impacts and mitigation measures (ways to fix), are permanently rescinded.
Funding for Low-Carbon Transportation Materials Grants, used to incentivize the use of low-emissions materials in projects related to federal highways and lands and tribal transportation facilities, is permanently rescinded.
100007 - AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL STAFFING AND MODERNIZATION
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $12,760,000,000 will be added for replacement of air traffic control towers, radar systems, telecommunications infrastructure, and for runway safety projects and air traffic controller recruitment, retention, and training.
It is important to note here that the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), under President Donald Trump, fired 400 personnel from the FAA in the first weeks of the new administration.
100008 - JOHN F. KENNEDY CENTER FOR THE PERFORMING ARTS
In addition to already-appropriated funds, $256,657,000 will be added for repairs and restoration to the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts.
TITLE XI -- COMMITTEE ON WAYS AND MEANS, "THE ONE, BIG, BEAUTIFUL BILL"
110000 - REFERENCES TO THE INTERNAL REVENUE CODE OF 1986, ETC.
Any discussion of amendments or repeals are in reference to the Internal Revenue Code of 1986.
PART 1 - PERMANENTLY PREVENTING TAX HIKES ON AMERICAN FAMILIES AND WORKERS
110001 - EXTENSION OF MODIFICATION RATES
Section 1 is amended to lower the percent tax rate for bracketed earners by the following percentages:
For some perspective, a single filer makes up to $11,925 for bracket 1, and $626,350 or more for bracket 7, meaning the first guy will pay $1,192.50 in taxes (and save nothing), but someone making $1 million a year will save $16,747.05 by this new amendment.
110002 - EXTENSION OF INCREASED STANDARD DEDUCTION AND TEMPORARY ENHANCEMENT
Section 63 is amended to increase the standard deduction to $24,000 for head of household, $16,000 for single filers, and $32,000 for married filing jointly.
110003 - TERMINATION OF DEDUCTION FOR PERSONAL EXEMPTIONS
Section 151 is amended to permanently repeal deductions for personal exemptions, which has not been in effect since 2018.
110004 - EXTENSION OF INCREASED CHILD TAX CREDIT AND TEMPORARY ENHANCEMENT
Dates in section 24 are extended, and the child tax credit of $2000 will be permanent.
110005 - EXTENSION OF DEDUCTION FOR QUALIFIED BUSINESS INCOME AND PERMANENT ENHANCEMENT
Section 199 is amended to increase the deductible amount of qualified business income or real estate investment from 20% to 23%.
110006 - EXTENSION OF INCREASED ESTATE AND GIFT TAX EXEMPTION AMOUNTS AND PERMANENT ENHANCEMENT
Section 2010 increases the lifetime gift tax exemption from $5 million to $15 million for single filers ($30 million filing jointly).
110007 - EXTENSION OF INCREASED ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM TAX EXEMPTION AND PHASE-OUT THRESHOLDS
Section 55 is amended to permanently increase the minimum exemption and phase-out thresholds (i.e. if you make below a certain amount you do not pay income tax).
110008 - EXTENSION OF LIMITATION ON DEDUCTION FOR QUALIFIED RESIDENCE OF INTEREST
Section 163 is amended to permanently lower the deduction for residence interest to $750,000.
110009 - EXTENSION OF LIMITATION ON CASUALTY LOSS DEDUCTION
Section 165 is amended to clarify that you can only itemize deductions for uncompensated personal casualty losses if there is a federally-declared disaster.
110010 - TERMINATION OF MISCELLANEOUS ITEMIZED DEDUCTION
Section 67 is amended to no longer include expenses like tax preparation, work-related travel, and uniforms in miscellaneous itemized deductions.
110011 - LIMITATION ON TAX BENEFIT OF ITEMIZED DEDUCTIONS
Section 68 is amended to reduce itemized deductions.
110012 - TERMINATION OF QUALIFIED BICYCLE COMMUTING REIMBURSEMENT EXCLUSIONS
Section 132 is amended to state that the $20/month employee bicycle expense reimbursement will now be taxable as income.
110013 - EXTENSION OF LIMITATION ON EXCLUSION AND DEDUCTION FOR MOVING EXPENSES
Section 217 is amended to remove deductions for moving expenses, except for active-duty members of the military.
110014 - EXTENSION OF LIMITATION ON WAGERING LOSSES
Section 165 is amended to state that any gambling deductions may not exceed winnings.
110015 - EXTENSION OF INCREASED LIMITATION ON CONTRIBUTIONS TO ABLE ACCOUNTS AND PERMANENT ENHANCEMENT
Section 529 is amended to permanently allow for additional contributions to Achieving a Better Life Experience (ABLE) accounts, a "tax-advantaged savings account for individuals with disabilities."
110016 - EXTENSIONS OF SAVERS CREDIT ALLOWED FOR ABLE CONTRIBUTIONS
Section 25B is amended to permanently allow beneficiaries of ABLE accounts to qualify for the Saver's Credit, a "federal tax credit that helps low- to moderate-income taxpayers save for retirement."
110017 - EXTENSION OF ROLLOVERS FROM QUALIFIED TUITION PROGRAMS TO ABLE ACCOUNTS PERMITTED
Section 529 is also amended so that beneficiaries of ABLE accounts can roll over their qualified tuition programs tax-free.
110018 - EXTENSION OF TREATMENT OF CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS PERFORMING SERVICES IN THE SINAI PENINSULA AND ENHANCEMENT TO INCLUDE ADDITIONAL AREAS
Section 11026 of Public Law 115-97 is amended to permanently include the Sinai Peninsula, Kenya, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Chad as "hazardous duty area" for tax purposes.
110019 - EXTENSION OF EXCLUSION FROM GROSS INCOME OF STUDENT LOANS DISCHARGED ON ACCOUNT OF DEATH OR DISABILITY
Section 108 is amended to permanently exclude any income resulting in discharge of student debt due to death or disability, but adds Social Security number requirements in order to claim the exclusion (i.e. if you don't have papers, you will be taxed; if you do, you won't).
PART 2 - ADDITIONAL TAX RELIEF FOR AMERICAN FAMILIES AND WORKERS
110101 - NO TAX ON TIPS
Sections 6041, 6050, and 6051 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 are amended to state that if you make less than $80,000/year you can deduct your tips from service jobs, such as restaurants, hospitality, and the beauty industry, as long as you have a social security number. If you do not have a social security number, meaning you are likely undocumented, you will have to pay the full taxes on your tips.
110102 - NO TAX ON OVERTIME
Section 225 is amended so that all non-exempt employees (i.e. not salaried or C-suite) can deduct overtime pay, but only the portion that is over their regular wage. For example, if you make $10/hour and for overtime you make $15/hour, you can only deduct $5/hour. This does not apply to anyone making over $80,000/year or who does not have a social security number. Thus undocumented workers will still be taxed on overtime pay.
110103 - ENHANCED DEDUCTION FOR SENIORS
Section 63 is amended to state that all seniors (age 65 or older) making $75,000 or less for single filers, and $150,000 or less for married filing jointly, are eligible for a $4000 deduction. This will not benefit low-income seniors who pay very little income tax, and is set to expire in 2028.
110104 - NO TAX ON CAR LOAN INTEREST
Section 163 states that you can deduct up to $10,000 on car loan interest from 2025 to 2028, but does not specify if this is the total amount for the 4 taxable years or if it is per year. You will not qualify if you make over $100,000 as a single filer, $200,000 filing jointly, or if your car was not assembled in the United States.
110105 - ENHANCEMENT OF EMPLOYER-PROVIDED CHILD CARE CREDIT
Section 45 is amended so that businesses can increase their child-care credit from 25% to 40% (50% for small businesses that make less than $31 million/year) and up to $500,000 (i.e. if the company spends $1.25 million on child care for employees they will receive the whole $500,000 credit).
110106 - EXTENSION AND ENHANCEMENT OF PAID FAMILY AND MEDICAL LEAVE CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to make permanent the Paid Family and Medical Leave (PFML) tax credit set to expire in 2025, which allows employers to claim wages paid to employees while on leave, as long as they don't make more than $96,000 (after which the employee is ineligible for PFML). This amendment will lower the employee eligibility work requirement for compensation from 1 year to 6 months.
110107 - ENHANCEMENT OF ADOPTION CREDIT
Section 23 is amended to state that up to $5000 of an adoption tax credit (which caps out at $16,810) can be refundable, but cannot be carried forward. Fees for domestic and international adoption typically range from $25,000 to $70,000 through an agency, and up to $40,000 for private adoptions.

110108 - RECOGNIZING INDIAN TRIBAL GOVERNMENTS FOR PURPOSES OF DETERMINING WHETHER A CHILD HAS SPECIAL NEEDS FOR PURPOSES OF THE ADOPTION CREDIT
Section 23 is further amended to give Native American Tribes the same ability as state governments to determine if a child has special needs when considering the adoption tax credit.
110109 - SCHOLARSHIP GRANTING ORGANIZATIONS
Section 117 is amended to allow businesses and individuals to receive up to a $5000 tax credit for donating to scholarship programs at private or religious elementary and secondary schools, as long as the students don't come from homes that make over 300% of the median gross income for their area.
110110 - ADDITIONAL ELEMENTARY, SECONDARY, AND HOME SCHOOL EXPENSES TREATED AS QUALIFIED HIGHER EDUCATION EXPENSES FOR PURPOSES OF 529 ACCOUNTS
Section 529 is amended to expand current 529 savings plan tax-advantaged accounts (state-sponsored savings plans to help save for future education expenses) to be used for curriculum, tutoring, and testing related to public, private, religious, or home schooling.
110111 - CERTAIN POSTSECONDARY CREDENTIALING EXPENSES TREATED AS QUALIFIED HIGHER EDUCATION EXPENSES FOR PURPOSES OF 529 ACCOUNTS
Section 529 is also amended to expand current 529 savings plan tax-advantaged accounts to be used for postsecondary (after high school) expenses. This, however, could impact a student's eligibility for need-based financial aid.

110112 - REINSTATEMENT OF PARTIAL DEDUCTION FOR CHARITABLE CONTRIBUTIONS OF INDIVIDUALS WHO DO NOT ELECT TO ITEMIZE
Section 170 is amended to allow those who don't itemize (subtract eligible expenses from Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)) to deduct up to $150 for single filers and $300 for married filing jointly for charitable donations. This is significantly lower than the Charitable Act, which was introduced in the Senate in 2025, which would allow for $1000 and $2000, respectively.
110113 - EXCLUSION FOR CERTAIN EMPLOYER PAYMENTS OF STUDENT LOANS UNDER EDUCATIONAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAMS MADE PERMANENT AND ADJUSTED FOR INFLATION
Section 127 is amended to make permanent the provision that allows the first $5,250 of employer-provided educational assistance to be excluded from an employee's taxable income.
110114 - EXTENSION OF RULES FOR TREATMENT OF CERTAIN DISASTER-RELATED PERSONAL CASUALTY LOSSES
This makes permanent section 304(b) of the Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2020, which states that losses due to disaster do not need to exceed 10% of your income, and taxpayers do not need to itemize in order to receive tax relief.
110115 - TRUMP (MAGA) ACCOUNTS
This provision creates "Money Accounts for Growth Advancement (MAGA)," savings accounts for children under the age of 8 to which their parents and relatives can contribute up to $5000 a year, while private foundations do not have a limit. The recipient may withdraw up to half the funds at age 18, but only for education, training, small-business loans, or to buy a house. They may withdraw the entire amount for any purpose at age 30. To be eligible, the child must be a U.S. citizen and at least one parent must provide their social security number.
110116 - TRUMP (MAGA) ACCOUNTS PILOT PROGRAM
This provision uses the MAGA as a pilot program, and the federal government will contribute $1000 to all savings accounts for babies born in Trump's second administration, managed by banks or investment firms, and immediately invested in the stock market on their behalf. Babies given a social security number at birth would be automatically enrolled, and parents or third-parties can contribute up to $5000 a year. The money can only be withdrawn for buying a home, for education-related expenses, or for starting a small business until the age of 30. Half the funds can be withdrawn at 18, but if money is misspent a 10% penalty will apply. If your family member or private contributor cannot afford to add to the account in order to pay for aforementioned expenses, you will not be able to withdraw the money until after age 30, when it can be used for any purpose.
PART 3 - INVESTING IN HEALTH OF AMERICAN FAMILIES AND WORKERS
110201 - TREATMENT OF HEALTH REIMBURSEMENT ARRANGEMENTS INTEGRATED WITH INDIVIDUAL MARKET COVERAGE
Section 9815 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to change the current health reimbursement arrangement (HRA) with new permitting regulations, and renames the policy as "Custom Health Option and Individual Care Expense (CHOICE)," which is meant to "bring more flexibility and customization to employer-provided health benefits." However, employees will lose their premium tax credits offered through the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare), which can result in higher out-of-pocket and overall healthcare costs.
110202 - PARTICIPANTS IN CHOICE ARRANGEMENT ELIGIBLE FOR PURCHASE OF EXCHANGE INSURANCE UNDER CAFETERIA PLAN
A "cafeteria plan (Section 125)" is an employee-sponsored benefit plan that allows employees to obtain pre-tax benefits like health insurance and retirement contributions. Section 125 is amended so that employees enrolled in a CHOICE arrangement can use a salary reduction to pay for health plan premiums purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace. While this, again, may bring more flexibility, employees will run the risk of forfeiting unused funds at the end of the plan year.
110203 - EMPLOYER CREDIT FOR CHOICE ARRANGEMENT
Small-business employers (50 or fewer employees) who participate in the CHOICE arrangement will receive a $1200-per-employee credit for the first year and $600 for the second year. However, leaning heavily into just Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (ICHRAs), which allow employers to provide tax-free reimbursements to employees, you run the risk of limiting accessibility to quality healthcare by skewing prices and leading to greater systemic issues.
110204 - INDIVIDUALS ENTITLED TO PART A OF MEDICARE BY REASON OF AGE ALLOWED TO CONTRIBUTE TO HEALTH SAVINGS ACCOUNTS
Section 223 is amended to state that seniors over 65 who still go to work and are eligible for Medicare Part A--which covers inpatient care, nursing homes, hospice (end-of-life) care, and some health care--can contribute to a Health Savings Account (HSA) as an add-on to your High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP). Parts B, C, and D cannot.
110205 - TREATMENT OF DIRECT PRIMARY CARE SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS
Section 223 is further amended so that individuals with HDHPs can enroll in Direct Primary Care (DPC) arrangements--which allows them to pay a flat monthly fee to their primary care provider, bypassing insurance--and use their HSAs to cover those DPC fees. However, DPCs only cover routine checkups and basic lab work, not major medical events. Therefore if they transfer out of an HDHP to a DPC, they may end up with astronomical out-of-pocket costs.
110206 - ALLOWANCE OF BRONCE AND CATASTROPHIC PLANS IN CONNECTION WITH HEALTH SAVINGS ACCOUNTS.
Section 223 is further amended so that all bronze and catastrophic health plans--low monthly cost, high out-of-pocket deductibles and copayments--can contribute to an HSA. However, this will disproportionately benefit high-income households, ignoring those who need care the most.
110207 - ON-SITE EMPLOYEE CLINICS
Section 223 is further amended to allow individuals who use worksite health clinics--which offer significant medical benefits for free or reduce cost--to contribute to an HSA, something the IRS wanted to avoid because it defeats the purpose of HSAs for paying high deductibles before your insurance kicks in.
110208 - CERTAIN AMOUNTS PAID FOR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, FITNESS, AND EXERCISE TREATED AS AMOUNTS PAID FOR MEDICAL CARE
Section 223 is further amended to allow HSAs to pay for health and fitness fees up to $500/year for individuals and $1000/year for families. However, what is considered "health and wellness" is undefined and would require extensive documentation for coverage.
110209 - ALLOW BOTH SPOUSES TO MAKE CATCH-UP CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE SAME HEALTH SAVING ACCOUNT
Section 223 is further amended to allow HSA-eligible spouses age 55 or older to contribute to the same HSA account, rather than separate accounts. There is some confusion, however, as to how the IRS would attribute the 6% excise (goods, services, and activities) tax on excess contributions that are combined.
110210 - FSA AND HRA TERMINATIONS OR CONVERSIONS TO FUND HSAS
Section 106 is amended to allow individuals to transfer the balance from Flexible Spending Arrangements (FSAs)--a "pre-tax benefit account that allows employees to set aside money from each paycheck for qualified medical and dependent care expenses”--or Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)--employer-funded health benefits that reimburse employees for qualified medical expenses--into an HSA when enrolling in an HDHP-HSA. But anyone who does not have an HDHP will lose access to a pre-tax HSA.
11211 - SPECIAL RULE FOR CERTAIN MEDICAL EXPENSES INCURRED BEFORE ESTABLISHMENT OF HEALTH SAVINGS ACCOUNT
Section 223 is further amended to allow any qualified medical expense (QME) within 60 days prior to establishing an HSA to be eligible. However, if a QME occurs prior to commencement of HDHP it will not be covered.
110212 - CONTRIBUTIONS PERMITTED IF SPOUSE HAS HEALTH FLEXIBLE SPENDING ARRANGEMENT
Section 223 is further amended to allow an individual to be eligible for an HSA even if their spouse is enrolled in a Flexible Spending Arrangement (FSA). This could lead to a lot of confusion, especially in older patients, when it comes to tax penalties and misuse of funds.'
110213 - INCREASE IN HEALTH SAVINGS ACCOUNT CONTRIBUTION LIMITATION FOR CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Section 223 is further amended to double the maximum contribution for HSAs to $8600 for individuals making under $75,000/year, and $17,100 for families making less than $150,000/year. The expansion of HSAs could potentially crowd out other healthcare programs, disadvantaging lower- and middle-income households, and benefitting those in a higher tax bracket.
110214 - REGULATIONS
This section gives the Secretary of Treasury (currently Scott Bessent) and the Secretary of Health and Human Services (currently Robert F. Kennedy Jr.) the right to make and enforce rules pertaining to this portion of the Big Beautiful Bill.
PART 1 - EXTENSION OF TAX CUTS AND JOBS ACT PERFORMS FOR RURAL AMERICA AND MAIN STREET
111001 - EXTENSION OF SPECIAL DEPRECIATION ALLOWANCE FOR CERTAIN PROPERTY
Section 168 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to raise the deductible of the cost of property used in trade or business from 40% to 100%.
111002 - DEDUCTION OF DOMESTIC RESEARCH AND EXPERIMENTAL EXPENDITURES
Section 174 is amended so that any research or experimental expenditures no longer need to deduct costs over a five-year period, but instead can do so immediately.
111003 - MODIFIED CALCULATION OF ADJUSTED TAXABLE INCOME FOR PURPOSES OF BUSINESS INTEREST DEDUCTION
Section 163 is amended to raise the cap on the deductibility of business interest expense by no longer accounting for deductions for depreciation (cost of property like equipment and machinery), amortization (paying off debt), and depletion (reduction of resources like oil, gas, minerals, or timber). This will lead to increased tax liability for businesses because they can deduct less of their interest expense.
111004 - EXTENSION OF DEDUCTION FOR FOREIGN-DERIVED INTANGIBLE INCOME AND GLOBAL INTANGIBLE LOW-TAXED INCOME
Section 250 is amended to keep the deduction for foreign-derived intangible income (intellectual property, not physical products, i.e. patents, trademarks, and copyrights within the U.S.) at 37.5% and global intangible low-taxed income (same, but overseas) at 50%. These were both set to decrease at the end of the year, thanks to the Biden Administration, but now run the risk of favoring overseas exports rather than domestic, offshoring jobs, and reducing domestic innovation.
111005 - EXTENSION OF BASE EROSION MINIMUM TAX AMOUNT
Section 59 is amended to keep the 10% (originally set to increase to 12.5% at the end of the year) base erosion anti-abuse tax, which limits international companies from shifting profits from the U.S. to low-tax countries, for businesses who make over $500 million a year. This will disproportionately benefit the wealthiest households who own a larger share of stocks, exacerbating income and wealth inequality.
111006 - EXCEPTION TO DENIAL OF DEDUCTION FOR BUSINESS MEALS
Section 274 is amended to provide an exception to the deduction limitation, allowing for 100% deduction for meals provided where they are essential to the core of the business (i.e. restaurants providing meals to employees during work hours). However, this could potentially be exploited without oversight, leading to tax avoidance.
PART 2 - ADDITIONAL TAX RELIEF FOR RURAL AMERICA AND MAIN STREET
111101 - SPECIAL DEPRECIATION ALLOWANCE FOR QUALIFIED PRODUCTION PROPERTY
Section 168 is amended to no longer require a 39-year depreciation deduction of nonresidential properties, and instead allow taxpayers to deduct 100% of their property, including factories and large structures, immediately as long as it is in the U.S., and as long as it does not include offices, research, or software engineering activities. This will give companies a major upfront swing in income, but may leave them without extra cash several years out, and won't allow them any benefits if tax rates change.
111102 - RENEWAL AND ENHANCEMENT OF OPPORTUNITY ZONES
Section 1400Z-1 is amended to change low-income "Opportunity Zones (OZs)" (economically-destressed communities defined by the U.S. Census), which are chosen by state governors in order to provide tax benefits and encourage investors, from 80% of the area median income to 70%. And unlike before, at least 33% of OZs must be entirely in rural areas, giving opportunity for investment on a 10% step-up basis when held at least 5 years.
111103 - INCREASED DOLLAR LIMITATIONS FOR EXPENSING OF CERTAIN DEPRECIABLE BUSINESS ASSETS
Section 179 is amended to increase the amount a taxpayer may expense the cost of a qualifying property (equipment, vehicles, building improvements) from $1 million to $2.5 million. This would favor larger businesses as well as wealthier individuals who own or have stakes in the business.
111104 - REPEAL OF REVISION TO DE MINIMIS RULES FOR THIRD PARTY NETWORK TRANSACTIONS
Section 6050W is amended to reinstate the Exception for De Minimis Payments, which eliminates all 1099 tax reporting unless a payee has earned more than $20,000 in 200 separate transactions, administering a third-party settlement organization. Previously the limit was $600.

111105 - INCREASE IN THRESHOLD FOR REQUIRING INFORMATION REPORTING WITH RESPECT TO CERTAIN PAYEES.
Section 6041 is amended to increase the reporting threshold for services by an independent contractor from $600 to $2000.
111106 - REPEAL OF EXCISE TAX ON INDOOR TANNING SERVICES
This section serves to remove the 10% excise tax on indoor tanning services which was originally intended to discourage tanning and help fund healthcare.
111107 - EXCLUSION OF INTEREST ON LOANS SECURED BY RURAL OR AGRICULTURAL REAL PROPERTY
This section serves to exclude up to 25% of the interest on rural or agricultural real estate loans. This would likely favor larger agricultural operations with access to substantial capital.
111108 - TREATMENT OF CERTAIN QUALIFIED SOUND RECORDING PRODUCTIONS
Section 181 is amended to allow taxpayers to expense up to $150,000/year of the costs of sound recording production and equipment.
111109 - MODIFICATIONS TO THE LOW-INCOME HOUSING CREDIT
Section 42 is amended to raise the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) 12.5% and lower bond-financing from 50% to 25%, and provide a 30% basis boost (tax credits) in Native American Communities. However, these benefits may flow to investors faster than they do low-income tenants.
111110 - INCREASED GROSS RECEIPTS THRESHOLD FOR SMALL MANUFACTURING BUSINESSES
Section 448 is amended to increase gross receipts of a manufacturing taxpayer (makes, sells, rents property) from below $25 million to $80 million in order to be exempt from business interest deductibility and accounting for inventory.
111111 - GLOBAL INTANGIBLE LOW-TAXED INCOME DETERMINED WITHOUT REGARD TO CERTAIN INCOME DERIVED FROM SERVICES PERFORMED IN THE VIRGIN ISLANDS
While most Global Intangible Low-Tax Income (GILTI) (taxable income earned from foreign profits) is taxed between 10.5% and 13.125%, the Virgin Islands (considered the world's top tax haven) will now be exempt.
PART 3 - INVESTING IN THE HEALTH OF RURAL AMERICA AND MAIN STREET
111112 - EXTENSION AND MODIFICATION OF CLEAN FUEL PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 45Z is amended to state that the previous tax credit offered for the production of transportation fuel, including aviation, now only exists for fuel made inside the U.S. However, this incentivizes only conventional biofuels industry and not necessarily clean fuels like biogenic sustainable aviation fuel.
111201 - EXPANDING THE DEFINITION OF RURAL EMERGENCY HOSPITAL UNDER THE MEDICARE PROGRAM
Section 1861 of the Social Security Act is amended so that rural hospitals that have closed between 2014-2020 may reopen under Rural Emergency Hospital (REH) designation (i.e. small facilities that provide emergency and observation services, but no in-patient beds). However, the distance between an REH and local area hospital can limit eligibility for increased outpatient payments, and facilities will likely have to invest in more transfer services for sicker patients.
PART 1 - WORKING FAMILIES OVER ELITES
112001 - TERMINATION OF PREVIOUSLY-OWNED CLEAN VEHICLE CREDIT
Section 25 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for previously-owned clean vehicles, which was either $4000 or 30% of the sale price of the vehicle. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112002 - TERMINATION OF THE CLEAN VEHICLE CREDIT
Section 30 is amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for new clean vehicles, which was $7,500. It was originally set to expire December, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112003 - TERMINATION OF QUALIFIED COMMERCIAL CLEAN VEHICLES CREDIT
Section 45 is amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for commercial clean vehicles, which was $7,500. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112004 - TERMINATION OF ALTERNATIVE FUEL VEHICLE REFUELING PROPERTY CREDIT
Section 30 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for refueling properties, which was 30% of the property. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112005 - TERMINATION OF ENERGY EFFICIENT HOME IMPROVEMENT CREDITS
Section 25 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for energy efficiency improvements (upgrading insulation, installing energy-efficient appliances, using smart thermostats), which was 30% of qualified improvements. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112006 - TERMINATION OF RESIDENTIAL CLEAN ENERGY CREDIT
Section 25 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for homeowner spending (solar electric, solar water, fuel cells, wind energy), which was 30% of expenditures. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112007 - TERMINATION OF NEW ENERGY EFFICIENT HOME CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for Energy Star homes considered "Zero Energy Ready" (renewable energy systems offset energy consumption), which was $5000. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112008 - PHASE-OUT AND RESTRICTIONS ON CLEAN ELECTRICITY PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to phase out the clean electricity production credit, which rewarded taxpayers who produce electricity from facilities determined to have greenhouse gas emissions less than zero. This program will be gone by 2031.
112009 - RESTRICTIONS ON CLEAN ELECTRICY INVESTMENT CREDIT
Section 48 is amended to phase out tax credits for investing in clean electricity and energy storage from facilities determined to have greenhouse gas emissions less than zero. This program will be gone by 2031.
112010 - REPEAL OF TRANSFERABILITY OF CLEAN FUEL PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 6418 is amended so that a taxpayer may not transfer tax credits for clean fuel production to another person.

112011 - RESTRICTIONS ON CARBON OXIDE SEQUESTRATION CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to repeal tax credits for capturing and disposing of carbon oxide (CO or CO2), which were up to $36 per metric ton and set to increase after 2026. No credit will be given after the enactment of this bill.
112012 - RESTRICTIONS ON ZERO-EMISSION NUCLEAR POWER PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for electricity produced by nuclear power plants. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2025.
112013 - TERMINATION OF CLEAN HYDROGEN PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for qualified clean hydrogen. It was originally set to expire January 1, 2033, and will now expire in 2025.
112014 - PHASE-OUT AND RESTRICTIONS ON ADVANCED MANUFACTURING PRODUCTION CREDIT
Section 45 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for inverters, solar and wind energy components, battery components, and critical minerals. It was originally set to expire December 31, 2032, and will now expire in 2027 for wind, and 2031 for all other components.
112015 - PHASE-OUT OF CREDIT FOR CERTAIN ENERGY PROPERTY
Section 48 is further amended to accelerate the expiration date for tax credits for geothermal heat pumps. It was originally set to expire January 1, 2035, and will now expire in 2031.
112016 - INCOME FROM HYDROGEN STORAGE, CARBON CAPTURE ADDED TO QUALIFYING INCOME OF CERTAIN PUBLICLY TRADED PARTNERSHIPS TREATED AS CORPORATIONS
Section 7704 is amended to expand what is considered "qualifying income" for publicly-traded partnerships (where shares can be bought and sold), including storage of liquid or compressed hydrogen and carbon-dioxide capture.
112017 - LIMITATION ON AMORITIZATION OF CERTAIN SPORTS FRANCHISES
Section 197 is amended to reduce amortization (paying off debt) deductions for sports-related intangibles (goodwill, franchise value, employment contracts, etc.) to 50% of the current deduction.
112018 - LIMITATION ON INDIVIDUAL DEDUCTIONS FOR CERTAIN STATE AND LOCAL TAXES, ETC.
Section 275 is amended to increase the State and Local Tax (SALT) cap--which allows taxpayers to itemize deductions for state and local taxes up to $10,000, and was set to expire in 2025--to $30,000 and will extend it permanently.
112019 - EXCESSIVE EMPLOYEE REMUNERATION FROM CONTROLLED GROUP MEMBERS AND ALLOCATION OF DEDUCTION
Section 162 is amended to add limitations to a highly-paid employee's (CEO, CFO, COO, etc.) ability to deduct his or her compensation.
112020 - EXPANDING APPLICATION OF TAX ON EXCESS COMPENSATION WITHIN TAX-EXEMPT ORGANIZATIONS
Section 4960 is amended to omit former highly-paid employees (up to $1 million/year) from excise tax on excess compensation, and include only current employees.
112021 - MODIFICATION OF EXCISE TAX ON INVESTMENT INCOME OF CERTAIN PRIVATE COLLEGES AND UNIVERSITIES
Section 4968 is amended to increase the current 1.4% excise tax imposed on educational institutions for investment income to the following tiered system:
112022 - INCREASE IN RATE OF TAX ON NET INVESTMENT INCOME OF CERTAIN PRIVATE FOUNDATIONS
Section 4940 is amended to increase the current 1.39% excise tax imposed on private foundations for investment income to the following tiered system:
112023 - CERTAIN PURCHASES OF EMPLOYEE-OWNED STOCK DISREGARDED FOR PURPOSES OF FOUNDATION TAX ON EXCESS BUSINESS HOLDINGS
Section 4943 is amended to state that any stocks repurchased by a company from a previous employee are considered "outstanding" (currently owned by shareholders), and should be included in the 20% limitation on voting stock (number of employees allowed to own stock in a company).
112024 - UNRELATED BUSINESS TAXABLE INCOME INCREASED BY AMOUNT OF CERTAIN FRINGE BENEFIT EXPENSES FOR WHICH DEDUCTION IS DISALLOWED
Section 512 is amended to include employee transportation benefits (transit pass, vanpooling, parking, etc.) in taxable income. This was previously not included.
112025 - NAME AND LOGO ROYALTIES TREATED AS UNRELATED BUSINESS TAXABLE INCOME
Section 512 is further amended to include the sale or licensing of a company logo in taxable income. This was previously not included.
112026 - EXCLUSION OF RESEARCH INCOME LIMITED TO PUBLICLY AVAILABLE RESEARCH
Section 512 is further amended to include any non-profit research freely available to the public, including income from private research, to be included in taxable income. This was previously not included.
112027 - LIMITATION ON EXCESS BUSINESS LOSSES OF NONCORPORATE TAXPAYERS
This sections makes the previous provision that allowed for no deductions for excess business loss (amount your deductibles exceed your gross income) permanent.
112028 - 1-PERCENT FLOOR ON DEDUCTION OF CHARITABLE CONTRIBUTIONS MADE BY CORPORATIONS
Section 170 is amended to reduce the amount of taxable income a company can deduct for charitable contributions from 10% to 1%.
112029 - ENFORCEMENT OF REMEDIES AGAINST UNFAIR FOREIGN TAXES
This section defines the U.S. government's response to "unfair taxes" imposed by a foreign government, as determined by the Secretary of Treasury (currently Scott Bessent), and will raise taxes on those governments and entities in response.
112030 - REDUCTION OF EXCISE TAX ON FIREARMS SILENCERS
Section 5845 is amended to remove the transfer tax (ownership from one individual to another) on firearm silencers.
112031 - MODIFICATIONS TO DE MINIMIS ENTRY PRIVILEGE FOR COMMERCIAL SHIPMENTS
Section 321 of the Tariff Act of 1930 is amended to remove the standard of products valued at under $800 entering the U.S. duty-free, and instead will increase penalties for violators.
112032 - LIMITATION ON DRAWBACK OF TAXES PAID WITH RESPECT TO SUBSTITUTED MERCHANDISE
This section states that you cannot claim a refund for excise (goods, services, or activities) tax on imported tobacco unless the excise tax was actually paid on exported goods.
PART 2 - REMOVING TAXPAYER BENEFITS FOR ILLEGAL IMMIGRANTS
112101 - PERMITTING PREMIUM TAX CREDIT ONLY FOR CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Section 36 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended to exclude from premium tax credits individuals who are "lawfully present" in the U.S. and change the terminology to "lawful permanent residents," which includes certain Cuban immigrants and people living in the U.S. through the Compact of Free Association, a relationship between the U.S. and Pacific Island sovereign states. This change will restrict low- and middle-income families from being eligible for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
112102 - CERTAIN ALIENS TREATED AS INELIGIBLE FOR PREMIUM TAX CREDIT
Section 36 is further amended to exclude from tax credits individuals who are "lawfully present" in the U.S., including those here due to asylum (political refugee), parole, temporary protected status (TPS) (foreign nationals unable to return due to unsafe conditions), deferred enforced departure (similar to TPS but under the President's discretion), and withholding of removal (U.S. agrees not to deport due to persecution based on race, religion, or politics). This change will prohibit the aforementioned individuals from using premium tax credits to purchase health insurance under the ACA.
112103 - DISALLOWING PREMIUM TAX CREDIT DURING PERIODS OF MEDICAID INELIGIBILITY DUE TO ALIEN STATUS
Section 42 of the Social Security Act of 1935 is amended to remove eligibility for anyone who is over the 100% federal poverty level from receiving Medicaid, as well as undocumented immigrants below the poverty level, and those currently in the 5-year Medicaid waiting period due to immigration status. This change will prohibit the aforementioned individuals from using premium tax credits to purchase health insurance under the ACA.
112104 - LIMITING MEDICARE COVERAGE OF CERTAIN INDIVIDUALS
Chapter 36 is further amended to exclude individuals who are "lawfully present" in the U.S. from Medicare eligibility, and include only those who are permanent residents.
112105 - EXCISE TAX ON REMITTANCE TRANSFERS
Chapter 36 is further amended to add an excise tax to payments sent back home by immigrants to their families. These will be upfront payments when money is wired to other countries from the U.S.
112106 - SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER REQUIREMENTS FOR AMERICAN OPPORTUNITY AND LIFETIME LEARNING CREDITS
Section 25 is amended so that a student, taxpayer, or spouse must have a valid social security number or taxpayer identification number (TIN) in order to claim the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) ($2500 for college tuition, books, and fees) or Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) ($2000 for college tuition, books, and fees). Undocumented immigrants, whether or not they pay taxes, will not be eligible for these credits.
PART 3 - PREVENTING FRAUD, WASTE, AND ABUSE
112201 - REQUIRING EXCHANGE VERIFICATION OF ELIGIBILITY FOR HEALTH PLAN
Section 36 is further amended to require yearly eligibility audits in order to enroll for coverage on the Health Exchange. This will inevitably delay financial assistance for applicants while they wait for eligibility confirmation every year, leading to loss of coverage.
112202 - DISALLOWING PREMIUM TAX CREDIT IN CASE OF CERTAIN COVERAGE ENROLLED IN DURING SPECIAL ENROLLMENT PERIOD
Section 36 is further amended to exclude anyone enrolling for Medicare or Medicaid during the Special Enrollment period (extended time outside the normal Open Enrollment period), which includes anyone with income below 150% of the federal poverty line, from receiving premium tax credits.
112203 - ELIMINATING LIMITATION ON RECAPTURE OF ADVANCE PAYMENT OF PREMIUM TAX CREDIT
Section 36 is further amended to remove the limit on excess premium tax credits an individual must pay if they misestimate projected yearly income, and requires them to reimburse the IRS for the full amount. Excess tax credits could be due to a change in income (new job, raise), changes in family size, or becoming eligible for health coverage through your work.
112204 - IMPLEMENTING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE TOOLS FOR PURPOSES OF REDUCING AND RECOUPING IMPROPER PAYMENTS UNDER MEDICARE
Section 42 of the Social Security Act of 1935 is further amended to give $25 million to the Secretary of Health and Human Services (currently Robert F. Kennedy Jr.) to work with Artificial Intelligence (AI) contractors to track down overpayments to individuals on Medicare, and require them to pay that amount back to the government. The average person on Medicare is 70.7 years-old. The average person on Medicare makes less than $36,000/year.
112205 - ENFORCEMENT PROVISIONS WITH RESPECT TO COVID-RELATED EMPLOYEE RETENTION CREDITS
This section raises the normal penalties for understatement of tax liability (declaring less income than you made) specifically for COVID-related Employee Retention Tax Credits (ERTC), which covered employees affected during the COVID-19 pandemic.
112206 - EARNED INCOME TAX CREDIT REFORMS
Chapter 77 is amended to put stricter standards in place when it comes to duplicate Earned Income Tax Credit claims (benefits low- to moderate-income families with children or other dependents). If a child is added, in error, twice, the IRS can withhold refunds and the Secretary of Treasury (currently Scott Bessent) has the ability to access the filer's payroll for verification of income as a means of hunting down fraud.
112207 - TASK FORCE ON TERMINATION OF DIRECT FILE
This section terminates the Direct File Program, which allows 25 participating states to file their taxes online for free, and will instead have the IRS and private sectors (certified public accountants (CPAs), agencies, and software like TurboTax and H&R Block) work together to provide free services. However, these "free" services (as most of us are aware) are only free up to a point and then charge anywhere from $60 to hundreds of dollars to file our taxes online.
112208 - POSTPONEMENT OF TAX DEADLINES FOR HOSTAGES AND INDIVIDUALS WRONGLY DETAINED ABROAD
This section aims to extend tax deadlines for those in combat, hostages, and those who are wrongfully detained. However, there is an automatic extension program already in place for those in active combat, and there is currently an automatic extension for hostages or those in a terroristic situation, and of course the latter is based on opinion and the courts, and thus may be biased as to who gets an extension and/or refund and who does not.
112209 - TERMINATION OF TAX-EXEMPT STATUS OF TERRORIST SUPPORTING ORGANIZATIONS
Currently the IRS can revoke recognition of a group's tax-exempt status after examination and period of time for appeal. However, according to this bill, the Secretary of Treasury (currently Scott Bessent) has the authority to declare any tax-exempt group a "terrorist organization" and remove its tax-exempt designation. This could put any churches, synagogues, food banks, and other charitable organizations at risk for helping migrant communities that are listed under broad, sweeping declarations.
112210 - INCREASE IN PENALTIES FOR UNAUTHORIZED DISCLOSURES OF TAXPAYER INFORMATION
This section serves to increase the fine for unauthorized disclosure of taxpayer information from $5,000 to $250,000, with a maximum imprisonment of 10 years. This is in clear contradiction to the activities behind closed doors at the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), where unqualified agents had access to all IRS data, putting taxpayer information at risk.
112211 - RESTRICTION ON REGULATION OF CONTINGENCY FEES WITH RESPECT TO TAX RETURNS, ETC.
Contingency fees (those charged by tax preparers with the assumption of monies gained after your return is accepted by the IRS) are highly discouraged because they can be used to maximize refunds, but often include fraudulent activities and abuse of funds. However, this bill states that the Treasury Department can no longer regulate, prohibit, or restrict the use of contingency fees when preparing tax returns.
113001 - MODIFICATION OF LIMITATION ON THE PUBLIC DEBT
The current debt limit ($36.1 trillion) was established on January 2, 2025 in the last days of the Biden Administration. This is the maximum amount of money the U.S. Treasury can borrow. The “Big Beautiful Bill,” however, provides that the U.S. Treasury can raise that debt limit by another $4 trillion.
Congratulations, you’ve read the whole “Big Beautiful Bill” (something most congresspeople have not)! Now please, share, educate, and shout it to the rooftops so your friends and loved ones understand what we’re up against.
If you’d like to read the entire bill, you can do that here:
The Big, Beautiful Bill
Ellie is an author, editor, and owner of Red Pencil Transcripts, and works with filmmakers, podcasts, and journalists all over the world. She lives with her family just outside of New York City.
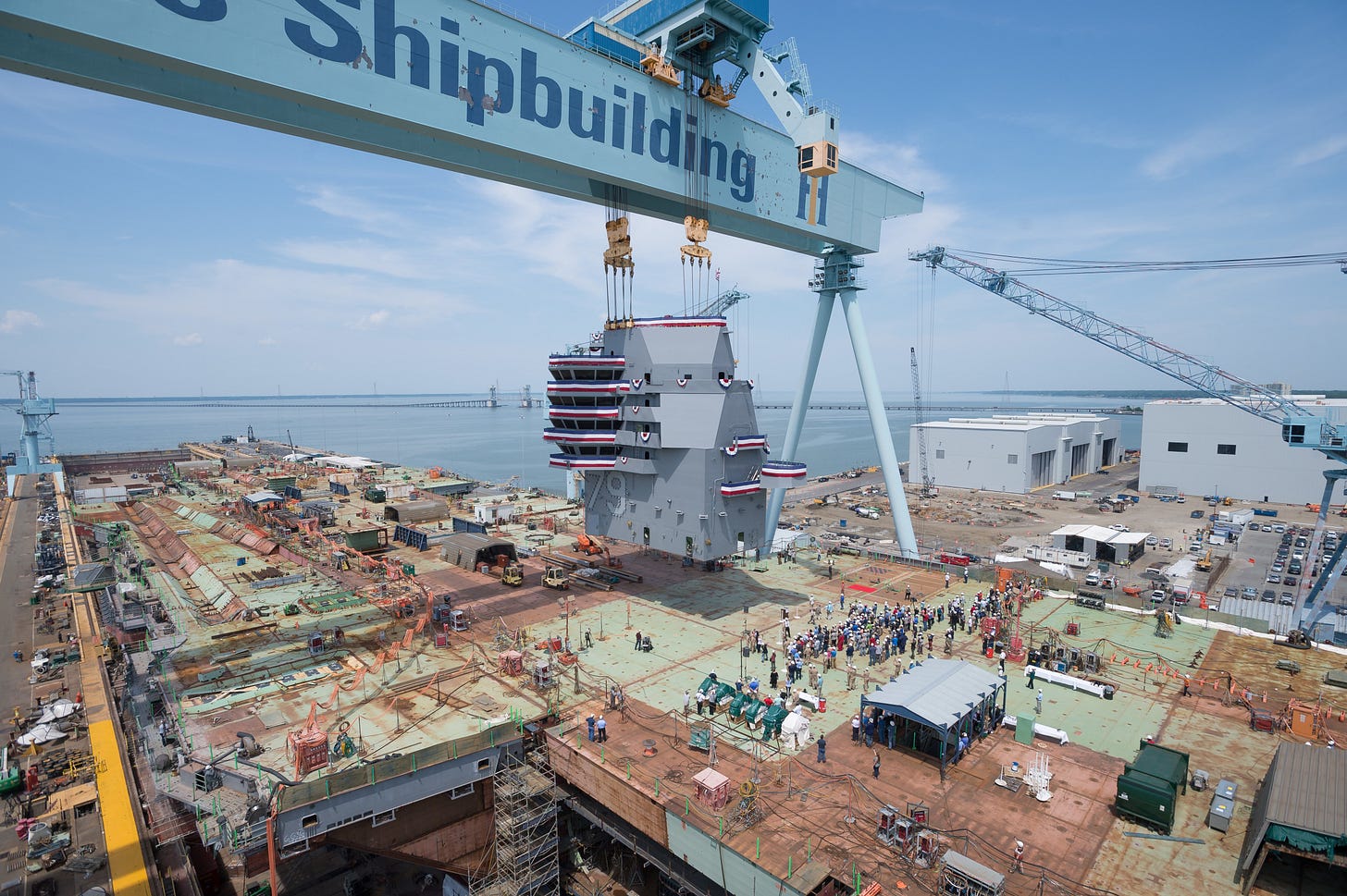
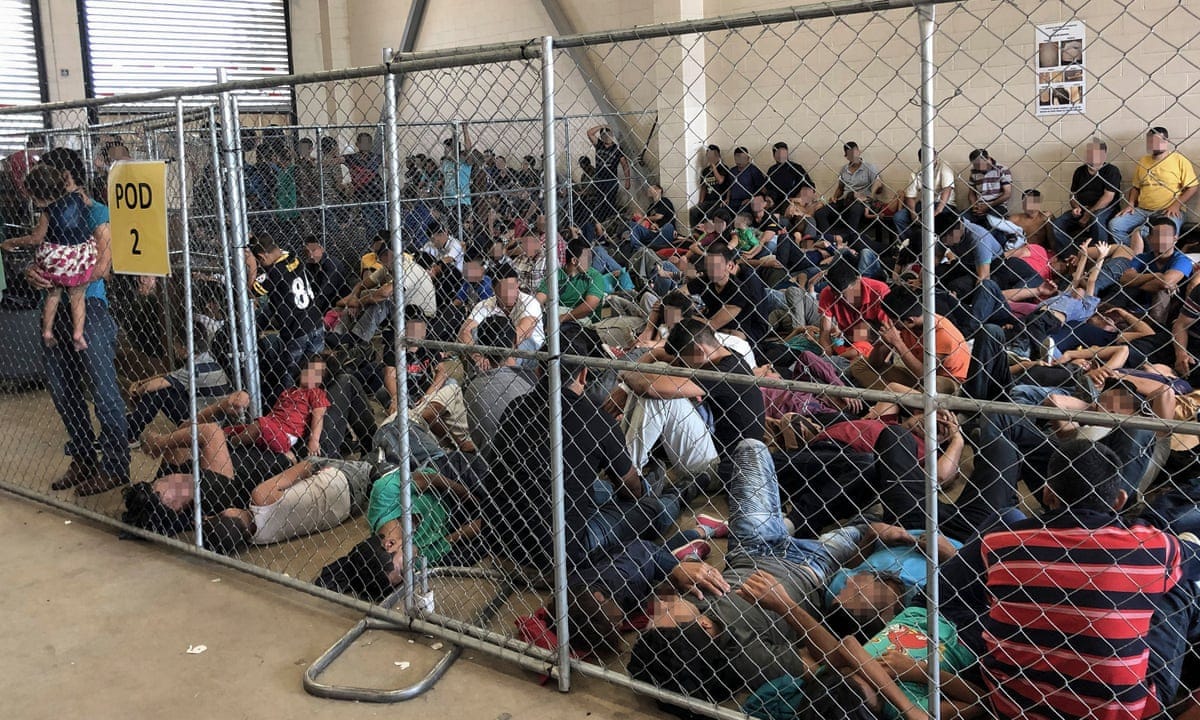
























































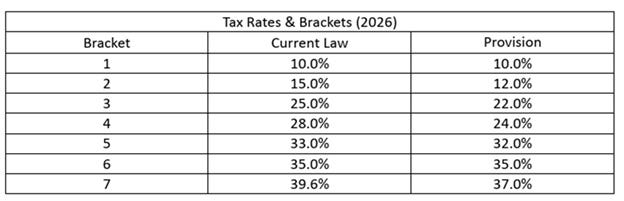

























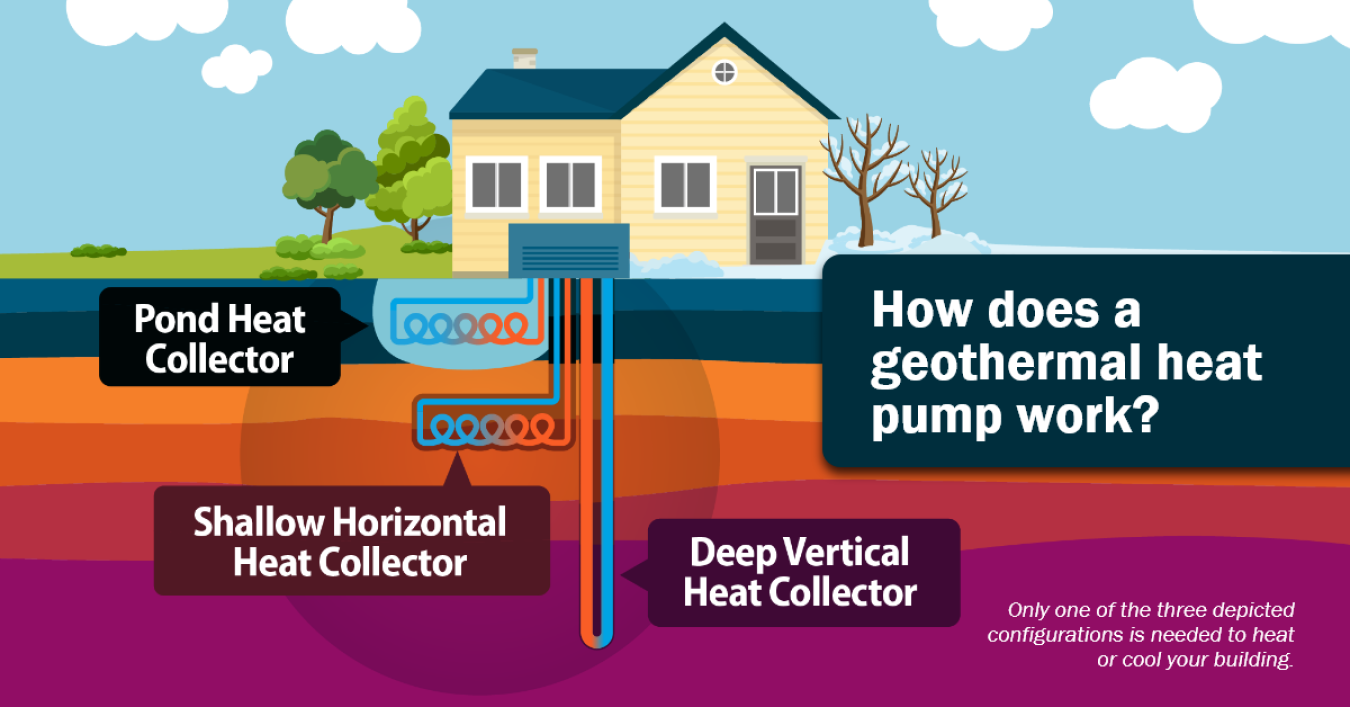



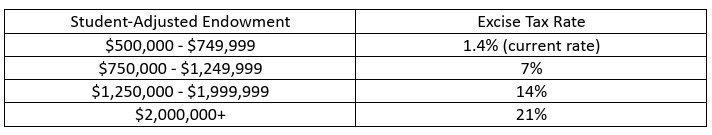










Wow! You put all that together quickly. I can’t imagine how many hours you must have invested in doing this. Thank you once again. Get some rest now.
These funds are excessive to maintain border issues. Someone stands to profit bigly from these funds and our taxpayer money, and it does nothing to change issues at borders, but merely puts more dollars in private hands!